Methionine sulfoxide reductase B1 (MsrB1) recovers TRPM6 channel activity during oxidative stress
- PMID: 20584906
- PMCID: PMC2924009
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.103655
Methionine sulfoxide reductase B1 (MsrB1) recovers TRPM6 channel activity during oxidative stress
Abstract
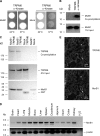
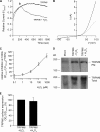
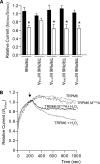
Mg(2+) is an essential ion for many cellular processes, including protein synthesis, nucleic acid stability, and numerous enzymatic reactions. Mg(2+) homeostasis in mammals depends on the equilibrium between intestinal absorption, renal excretion, and exchange with bone. The transient receptor potential melastatin type 6 (TRPM6) is an epithelial Mg(2+) channel, which is abundantly expressed in the luminal membrane of the renal and intestinal cells. It functions as the gatekeeper of transepithelial Mg(2+) transport. Remarkably, TRPM6 combines a Mg(2+)-permeable channel with an alpha-kinase domain. Here, by the Ras recruitment system, we identified methionine sulfoxide reductase B1 (MsrB1) as an interacting protein of the TRPM6 alpha-kinase domain. Importantly, MsrB1 and TRPM6 are both present in the renal Mg(2+)-transporting distal convoluted tubules. MsrB1 has no effect on TRPM6 channel activity in the normoxic conditions. However, hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) decreased TRPM6 channel activity. Co-expression of MsrB1 with TRPM6 attenuated the inhibitory effect of H(2)O(2) (TRPM6, 67 +/- 5% of control; TRPM6 + MsrB1, 81 +/- 5% of control). Cell surface biotinylation assays showed that H(2)O(2) treatment does not affect the expression of TRPM6 at the plasma membrane. Next, mutation of Met(1755) to Ala in TRPM6 reduced the inhibitory effect of H(2)O(2) on TRPM6 channel activity (TRPM6 M1755A: 84 +/- 10% of control), thereby mimicking the action of MsrB1. Thus, these data suggest that MsrB1 recovers TRPM6 channel activity by reducing the oxidation of Met(1755) and could, thereby, function as a modulator of TRPM6 during oxidative stress.
Figures
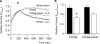
Similar articles
-
RACK1 inhibits TRPM6 activity via phosphorylation of the fused alpha-kinase domain.Curr Biol. 2008 Feb 12;18(3):168-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.12.058. Curr Biol. 2008. PMID: 18258429
-
Regulation of the epithelial Mg2+ channel TRPM6 by estrogen and the associated repressor protein of estrogen receptor activity (REA).J Biol Chem. 2009 May 29;284(22):14788-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808752200. Epub 2009 Mar 26. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19329436 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species Downregulate Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 6 Expression Mediated by the Elevation of miR-24-3p in Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells.Cells. 2021 Jul 26;10(8):1893. doi: 10.3390/cells10081893. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440664 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into the molecular regulation of the epithelial magnesium channel TRPM6.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2008 Jul;17(4):373-8. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e328303e184. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2008. PMID: 18660673 Review.
-
Epithelial Mg2+ channel TRPM6: insight into the molecular regulation.Magnes Res. 2009 Sep;22(3):127-32. Magnes Res. 2009. PMID: 19780399 Review.
Cited by
-
Redox Regulation of the NOR Transcription Factor Is Involved in the Regulation of Fruit Ripening in Tomato.Plant Physiol. 2020 Jun;183(2):671-685. doi: 10.1104/pp.20.00070. Epub 2020 Mar 31. Plant Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32234754 Free PMC article.
-
Selenoproteins: molecular pathways and physiological roles.Physiol Rev. 2014 Jul;94(3):739-77. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00039.2013. Physiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24987004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Rare Case of Neonatal Hypomagnesemia with Secondary Hypocalcemia Caused by a Novel Homozygous TRPM6 Gene Variant.Am J Case Rep. 2024 Mar 26;25:e942498. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.942498. Am J Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38528672 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometric analysis of TRPM6 and TRPM7 from small intestine of omeprazole-induced hypomagnesemic rats.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 29;12:947899. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.947899. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36110961 Free PMC article.
-
Methionine sulfoxide reductase A is a stereospecific methionine oxidase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 28;108(26):10472-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1101275108. Epub 2011 Jun 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21670260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vetter T., Lohse M. J. (2002) Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 11, 403–410 - PubMed
-
- Grubbs R. D., Maguire M. E. (1987) Magnesium 6, 113–127 - PubMed
-
- Romani A., Scarpa A. (1992) Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 298, 1–12 - PubMed
-
- Konrad M., Schlingmann K. P., Gudermann T. (2004) Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 286, F599–F605 - PubMed
-
- Grimellec C. L., Poujeol P., Rouffignia C. (1975) Pflugers. Arch. 354, 117–131 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

