Clearance of apoptotic cells: implications in health and disease
- PMID: 20584912
- PMCID: PMC2894449
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201004096
Clearance of apoptotic cells: implications in health and disease
Abstract
Recent advances in defining the molecular signaling pathways that regulate the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells have improved our understanding of this complex and evolutionarily conserved process. Studies in mice and humans suggest that the prompt removal of dying cells is crucial for immune tolerance and tissue homeostasis. Failed or defective clearance has emerged as an important contributing factor to a range of disease processes. This review addresses how specific molecular alterations of engulfment pathways are linked to pathogenic states. A better understanding of the apoptotic cell clearance process in healthy and diseased states could offer new therapeutic strategies.
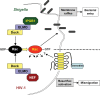
Figures

References
-
- A-Gonzalez N., Bensinger S.J., Hong C., Beceiro S., Bradley M.N., Zelcer N., Deniz J., Ramirez C., Díaz M., Gallardo G., et al. 2009. Apoptotic cells promote their own clearance and immune tolerance through activation of the nuclear receptor LXR. Immunity. 31:245–258 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.06.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ait-Oufella H., Kinugawa K., Zoll J., Simon T., Boddaert J., Heeneman S., Blanc-Brude O., Barateau V., Potteaux S., Merval R., et al. 2007. Lactadherin deficiency leads to apoptotic cell accumulation and accelerated atherosclerosis in mice. Circulation. 115:2168–2177 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.662080 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ait-Oufella H., Pouresmail V., Simon T., Blanc-Brude O., Kinugawa K., Merval R., Offenstadt G., Lesèche G., Cohen P.L., Tedgui A., Mallat Z. 2008. Defective mer receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in bone marrow cells promotes apoptotic cell accumulation and accelerates atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 28:1429–1431 10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.169078 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

