Interleukin-17A during local and systemic Staphylococcus aureus-induced arthritis in mice
- PMID: 20584972
- PMCID: PMC2937437
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00385-10
Interleukin-17A during local and systemic Staphylococcus aureus-induced arthritis in mice
Abstract
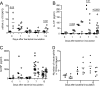
Staphylococcus aureus is one of the dominant pathogens that induce septic arthritis in immunocompromised hosts, e.g., patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis treated with immunosuppressive drugs. S. aureus-induced arthritis leads to severe joint destruction and high mortality despite antibiotic treatment. Recently, interleukin-17A (IL-17A) has been discovered to be an important mediator of aseptic arthritis both in mice and humans, but its function in S. aureus-induced arthritis is largely unknown. Here, we investigated the role of IL-17A in host defense against arthritis following systemic and local S. aureus infection in vivo. IL-17A knockout mice and wild-type mice were inoculated systemically (intravenously) or locally (intra-articularly) with S. aureus. During systemic infection, IL-17A knockout mice lost significantly more weight than the wild-type mice did, but no differences were found in the mortality rate. The absence of IL-17A had no impact on clinical arthritis development but led to increased histopathological erosivity late during systemic S. aureus infection. Bacterial clearance in kidneys was increased in IL-17A knockout mice compared to the level in wild-type mice only 1 day after bacterial inoculation. During systemic S. aureus infection, serum IL-17F protein levels and mRNA levels in the lymph nodes were elevated in the IL-17A knockout mice compared to the level in wild-type mice. In contrast to systemic infection, the IL-17A knockout mice had increased synovitis and erosions and locally decreased clearance of bacteria 3 days after local bacterial inoculation. On the basis of these findings, we suggest that IL-17A is more important in local host defense than in systemic host defense against S. aureus-induced arthritis.
Figures
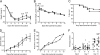

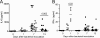


Similar articles
-
Neutrophils: Beneficial and Harmful Cells in Septic Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 5;19(2):468. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020468. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29401737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-33 Receptor (ST2) Deficiency Improves the Outcome of Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Septic Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2018 May 16;9:962. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00962. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29867945 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 15 mediates joint destruction in Staphylococcus aureus arthritis.J Infect Dis. 2012 Sep 1;206(5):687-96. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis295. Epub 2012 Apr 16. J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22508940
-
Role of interleukin-17A in cell-mediated protection against Staphylococcus aureus infection in mice immunized with the fibrinogen-binding domain of clumping factor A.Infect Immun. 2010 Oct;78(10):4234-42. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00447-10. Epub 2010 Aug 2. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20679443 Free PMC article.
-
Septic arthritis: immunopathogenesis, experimental models and therapy.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2014 May 6;20:19. doi: 10.1186/1678-9199-20-19. eCollection 2014. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24822058 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A cytokine-centric view of the pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune arthritis.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011 Dec;31(12):927-40. doi: 10.1089/jir.2011.0094. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011. PMID: 22149412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophils: Beneficial and Harmful Cells in Septic Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 5;19(2):468. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020468. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29401737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fracture biomechanics influence local and systemic immune responses in a murine fracture-related infection model.Biol Open. 2021 Sep 15;10(9):bio057315. doi: 10.1242/bio.057315. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Biol Open. 2021. PMID: 34240122 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus aureus-dependent septic arthritis in murine knee joints: local immune response and beneficial effects of vaccination.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 30;6:38043. doi: 10.1038/srep38043. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27901071 Free PMC article.
-
Bacteria and Host Interplay in Staphylococcus aureus Septic Arthritis and Sepsis.Pathogens. 2021 Feb 3;10(2):158. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020158. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33546401 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bremell, T., S. Lange, L. Svensson, E. Jennische, K. Grondahl, H. Carlsten, and A. Tarkowski. 1990. Outbreak of spontaneous staphylococcal arthritis and osteitis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 33:1739-1744. - PubMed
-
- Chabaud, M., J. M. Durand, N. Buchs, F. Fossiez, G. Page, L. Frappart, and P. Miossec. 1999. Human interleukin-17: a T cell-derived proinflammatory cytokine produced by the rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 42:963-970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

