Immunization with the Haemophilus ducreyi hemoglobin receptor HgbA with adjuvant monophosphoryl lipid A protects swine from a homologous but not a heterologous challenge
- PMID: 20584974
- PMCID: PMC2937461
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00217-10
Immunization with the Haemophilus ducreyi hemoglobin receptor HgbA with adjuvant monophosphoryl lipid A protects swine from a homologous but not a heterologous challenge
Abstract
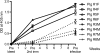
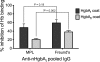
Haemophilus ducreyi, the etiological agent of chancroid, has a strict requirement for heme, which it acquires from its only natural host, humans. Previously, we showed that a vaccine preparation containing the native hemoglobin receptor HgbA purified from H. ducreyi class I strain 35000HP (nHgbAI) and administered with Freund's adjuvant provided complete protection against a homologous challenge. In the current study, we investigated whether nHgbAI dispensed with monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL), an adjuvant approved for use in humans, offered protection against a challenge with H. ducreyi strain 35000HP expressing either class I or class II HgbA (35000HPhgbAI and 35000HPhgbAII, respectively). Pigs immunized with the nHgbAI/MPL vaccine were protected against a challenge from homologous H. ducreyi strain 35000HPhgbAI but not heterologous strain 35000HPhgbAII, as evidenced by the isolation of only strain 35000HPhgbAII from nHgbAI-immunized pigs. Furthermore, histological analysis of the lesions showed striking differences between mock-immunized and nHgbAI-immunized animals challenged with strains 35000HPhgbAI but not those challenged with strain 35000HPhgbAII. Mock-immunized pigs were not protected from a challenge by either strain. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) activity of the nHgbAI/MPL antiserum was lower than the activity of antiserum from animals immunized with the nHgbAI/Freund's vaccine; however, anti-nHgbAI from both studies bound whole cells of 35000HPhgbAI better than 35000HPhgbAII and partially blocked hemoglobin binding to nHgbAI. In conclusion, despite eliciting lower antibody ELISA activity than the nHgbAI/Freund's, the nHgbAI/MPL vaccine provided protection against a challenge with homologous but not heterologous H. ducreyi, suggesting that a bivalent HgbA vaccine may be needed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immunization with the Haemophilus ducreyi hemoglobin receptor HgbA protects against infection in the swine model of chancroid.Infect Immun. 2006 Apr;74(4):2224-32. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.4.2224-2232.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16552053 Free PMC article.
-
Passive immunization with a polyclonal antiserum to the hemoglobin receptor of Haemophilus ducreyi confers protection against a homologous challenge in the experimental swine model of chancroid.Infect Immun. 2011 Aug;79(8):3168-77. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00017-11. Epub 2011 Jun 6. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21646451 Free PMC article.
-
The Haemophilus ducreyi trimeric autotransporter adhesin DsrA protects against an experimental infection in the swine model of chancroid.Vaccine. 2014 Jun 24;32(30):3752-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.05.031. Epub 2014 May 18. Vaccine. 2014. PMID: 24844153 Free PMC article.
-
A Class I Haemophilus ducreyi Strain Containing a Class II hgbA Allele Is Partially Attenuated in Humans: Implications for HgbA Vaccine Efficacy Trials.Infect Immun. 2019 Jun 20;87(7):e00112-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00112-19. Print 2019 Jul. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31036601 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Interactions of the Skin Pathogen Haemophilus ducreyi With the Human Host.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 3;11:615402. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.615402. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33613541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunization with the Haemophilus ducreyi trimeric autotransporter adhesin DsrA with alum, CpG or imiquimod generates a persistent humoral immune response that recognizes the bacterial surface.Vaccine. 2016 Feb 24;34(9):1193-200. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.01.024. Epub 2016 Jan 24. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 26812077 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Risks Caused by Livestock Excrement: Current Research Status and Prospects.Microorganisms. 2023 Jul 27;11(8):1897. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11081897. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37630456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The anti-influenza M2e antibody response is promoted by XCR1 targeting in pig skin.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 9;7(1):7639. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07372-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28794452 Free PMC article.
-
A vaccine of L2 epitope repeats fused with a modified IgG1 Fc induced cross-neutralizing antibodies and protective immunity against divergent human papillomavirus types.PLoS One. 2014 May 6;9(5):e95448. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095448. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24802101 Free PMC article.
-
Defining Potential Vaccine Targets of Haemophilus ducreyi Trimeric Autotransporter Adhesin DsrA.Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2015 Apr;34(2):73-82. doi: 10.1089/mab.2014.0054. Monoclon Antib Immunodiagn Immunother. 2015. PMID: 25897604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Tawfiq, J. A., K. R. Fortney, B. P. Katz, A. F. Hood, C. Elkins, and S. M. Spinola. 2000. An isogenic hemoglobin receptor-deficient mutant of Haemophilus ducreyi is attenuated in the human model of experimental infection. J. Infect. Dis. 181:1049-1054. - PubMed
-
- Al-Tawfiq, J. A., A. C. Thornton, B. P. Katz, K. R. Fortney, K. D. Todd, A. F. Hood, and S. M. Spinola. 1998. Standardization of the experimental model of Haemophilus ducreyi infection in human subjects. J. Infect. Dis. 178:1684-1687. - PubMed
-
- Baldrick, P., D. Richardson, G. Elliott, and A. W. Wheeler. 2002. Safety evaluation of monophosphoryl lipid A (MPL): an immunostimulatory adjuvant. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 35:398-413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

