Islet beta-cell-specific MafA transcription requires the 5'-flanking conserved region 3 control domain
- PMID: 20584984
- PMCID: PMC2937551
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01396-09
Islet beta-cell-specific MafA transcription requires the 5'-flanking conserved region 3 control domain
Abstract
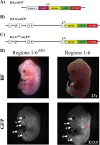
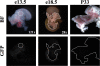
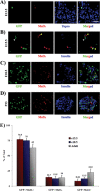
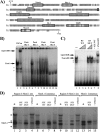
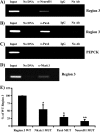
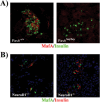
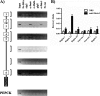
MafA is a key transcriptional activator of islet beta cells, and its exclusive expression within beta cells of the developing and adult pancreas is distinct among pancreatic regulators. Region 3 (base pairs -8118 to -7750 relative to the transcription start site), one of six conserved 5' cis domains of the MafA promoter, is capable of directing beta-cell-line-selective expression. Transgenic reporters of region 3 alone (R3), sequences spanning regions 1 to 6 (R1-6; base pairs -10428 to +230), and R1-6 lacking R3 (R1-6(DeltaR3)) were generated. Only the R1-6 transgene was active in MafA(+) insulin(+) cells during development and in adult cells. R1-6 also mediated glucose-induced MafA expression. Conversely, pancreatic expression was not observed with the R3 or R1-6(DeltaR3) line, although much of the nonpancreatic expression pattern was shared between the R1-6 and R1-6(DeltaR3) lines. Further support for the importance of R3 was also shown, as the islet regulators Nkx6.1 and Pax6, but not NeuroD1, activated MafA in gel shift, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and transfection assays and in vivo mouse knockout models. Lastly, ChIP demonstrated that Pax6 and Pdx-1 also bound to R1 and R6, potentially functioning in pancreatic and nonpancreatic expression. These data highlight the nature of the cis- and trans-acting factors controlling the beta-cell-specific expression of MafA.
Figures

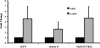
Similar articles
-
FoxA2, Nkx2.2, and PDX-1 regulate islet beta-cell-specific mafA expression through conserved sequences located between base pairs -8118 and -7750 upstream from the transcription start site.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;26(15):5735-43. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00249-06. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16847327 Free PMC article.
-
Hnf1α (MODY3) regulates β-cell-enriched MafA transcription factor expression.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Feb;25(2):339-47. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0362. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21193557 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved sequences in a tissue-specific regulatory region of the pdx-1 gene mediate transcription in Pancreatic beta cells: role for hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 beta and Pax6.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;22(13):4702-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.13.4702-4713.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12052878 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of insulin synthesis and secretion and pancreatic Beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013 Jan 1;9(1):25-53. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013. PMID: 22974359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PDX1, Neurogenin-3, and MAFA: critical transcription regulators for beta cell development and regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Nov 2;8(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0694-z. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29096722 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tshz1 Regulates Pancreatic β-Cell Maturation.Diabetes. 2015 Aug;64(8):2905-14. doi: 10.2337/db14-1443. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Diabetes. 2015. PMID: 25918232 Free PMC article.
-
Proper activation of MafA is required for optimal differentiation and maturation of pancreatic β-cells.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Dec;29(6):821-31. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2015.09.006. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26696512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MafA and MafB activity in pancreatic β cells.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Sep;22(9):364-73. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21719305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pax6 is crucial for β-cell function, insulin biosynthesis, and glucose-induced insulin secretion.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Apr;26(4):696-709. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1256. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22403172 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an apparently novel β-cell line-enriched 80-88 kDa transcriptional activator of the MafA and Pdx1 genes.J Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 8;288(6):3795-803. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.434282. Epub 2012 Dec 26. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23269676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artner, I., J. Le Lay, Y. Hang, L. Elghazi, J. C. Schisler, E. Henderson, B. Sosa-Pineda, and R. Stein. 2006. MafB: an activator of the glucagon gene expressed in developing islet alpha- and beta-cells. Diabetes 55:297-304. - PubMed
-
- Ashery-Padan, R., X. Zhou, T. Marquardt, P. Herrera, L. Toube, A. Berry, and P. Gruss. 2004. Conditional inactivation of Pax6 in the pancreas causes early onset of diabetes. Dev. Biol. 269:479-488. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R56 DK050203/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32 DK07563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK072504/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK072504/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK083160/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK083160/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK50203/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050203/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK60581/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060581/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007563/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
