The C-terminal region of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3a (eIF3a) promotes mRNA recruitment, scanning, and, together with eIF3j and the eIF3b RNA recognition motif, selection of AUG start codons
- PMID: 20584985
- PMCID: PMC2937525
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00280-10
The C-terminal region of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3a (eIF3a) promotes mRNA recruitment, scanning, and, together with eIF3j and the eIF3b RNA recognition motif, selection of AUG start codons
Abstract
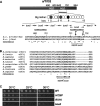
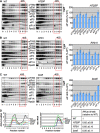
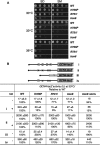
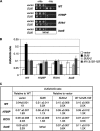
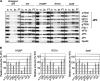
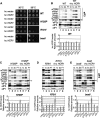
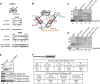
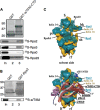
The C-terminal domain (CTD) of the a/Tif32 subunit of budding yeast eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 (eIF3) interacts with eIF3 subunits j/Hcr1 and b/Prt1 and can bind helices 16 to 18 of 18S rRNA, suggesting proximity to the mRNA entry channel of the 40S subunit. We have identified substitutions in the conserved Lys-Glu-Arg-Arg (KERR) motif and in residues of the nearby box6 element of the a/Tif32 CTD that impair mRNA recruitment by 43S preinitiation complexes (PICs) and confer phenotypes indicating defects in scanning and start codon recognition. The normally dispensable CTD of j/Hcr1 is required for its binding to a/Tif32 and to mitigate the growth defects of these a/Tif32 mutants, indicating physical and functional interactions between these two domains. The a/Tif32 CTD and the j/Hcr1 N-terminal domain (NTD) also interact with the RNA recognition motif (RRM) in b/Prt1, and mutations in both subunits that disrupt their interactions with the RRM increase leaky scanning of an AUG codon. These results, and our demonstration that the extreme CTD of a/Tif32 binds to Rps2 and Rps3, lead us to propose that the a/Tif32 CTD directly stabilizes 43S subunit-mRNA interaction and that the b/Prt1-RRM-j/Hcr1-a/Tif32-CTD module binds near the mRNA entry channel and regulates the transition between scanning-conducive and initiation-competent conformations of the PIC.
Figures



References
-
- Algire, M. A., D. Maag, and J. R. Lorsch. 2005. Pi release from eIF2, not GTP hydrolysis, is the step controlled by start-site selection during eukaryotic translation initiation. Mol. Cell 20:251-262. - PubMed
-
- Asano, K., L. Phan, J. Anderson, and A. G. Hinnebusch. 1998. Complex formation by all five homologues of mammalian translation initiation factor 3 subunits from yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 273:18573-18585. - PubMed
-
- Berthelot, K., M. Muldoon, L. Rajkowitsch, J. Hughes, and J. E. McCarthy. 2004. Dynamics and processivity of 40S ribosome scanning on mRNA in yeast. Mol. Microbiol. 51:987-1001. - PubMed
-
- Boeke, J. D., J. Trueheart, G. Natsoulis, and G. R. Fink. 1987. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 154:164-175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
