Different classes of antibiotics differentially influence shiga toxin production
- PMID: 20585113
- PMCID: PMC2935008
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01783-09
Different classes of antibiotics differentially influence shiga toxin production
Abstract
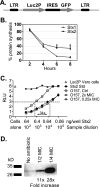
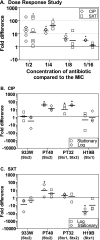
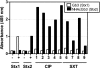
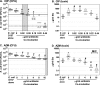
Shiga toxin (Stx) in Escherichia coli O157:H7 is encoded as a late gene product by temperate bacteriophage integrated into the chromosome. Phage late genes, including stx, are silent in the lysogenic state. However, stress signals, including some induced by antibiotics, trigger the phage to enter the lytic cycle, and phage replication and Stx production occur concurrently. In addition to the Stx produced by O157:H7, phage produced by O157:H7 can infect harmless intestinal E. coli and recruit them to produce Shiga toxin. To understand how antibiotics influence Stx production, Stx lysogens were treated with different classes of antibiotics in the presence or absence of phage-sensitive E. coli, and Stx-mediated inhibition of protein synthesis was monitored using luciferase-expressing Vero cells. Growth-inhibitory levels of antibiotics suppressed Stx production. Subinhibitory levels of antibiotics that target DNA synthesis, including ciprofloxacin (CIP) and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, increased Stx production, while antibiotics that target the cell wall, transcription, or translation did not. More Stx was produced when E. coli O157:H7 was incubated in the presence of phage-sensitive E. coli than when grown as a pure culture. Remarkably, very high levels of Stx were detected even when growth of O157:H7 was completely suppressed by CIP. In contrast, azithromycin significantly reduced Stx levels even when O157:H7 viability remained high.
Figures

References
-
- Endo, Y., K. Tsurugi, T. Yutsudo, Y. Takeda, T. Ogasawara, and K. Igarashi. 1988. Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes: RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur. J. Biochem. 171:45-50. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez, R. C., and A. A. Weiss. 1998. Serum resistance in bvg-regulated mutants of Bordetella pertussis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 163:57-63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

