The structure of tumor endothelial marker 8 (TEM8) extracellular domain and implications for its receptor function for recognizing anthrax toxin
- PMID: 20585457
- PMCID: PMC2887854
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011203
The structure of tumor endothelial marker 8 (TEM8) extracellular domain and implications for its receptor function for recognizing anthrax toxin
Abstract
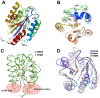
Anthrax toxin, which is released from the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus anthracis, is composed of three proteins: protective antigen (PA), lethal factor (LF), and edema factor (EF). PA binds a receptor on the surface of the target cell and further assembles into a homo-heptameric pore through which EF and LF translocate into the cytosol. Two distinct cellular receptors for anthrax toxin, TEM8/ANTXR1 and CMG2/ANTXR2, have been identified, and it is known that their extracellular domains bind PA with low and high affinities, respectively. Here, we report the crystal structure of the TEM8 extracellular vWA domain at 1.7 A resolution. The overall structure has a typical integrin fold and is similar to that of the previously published CMG2 structure. In addition, using structure-based mutagenesis, we demonstrate that the putative interface region of TEM8 with PA (consisting of residues 56, 57, and 154-160) is responsible for the PA-binding affinity differences between the two receptors. In particular, Leu56 was shown to be a key factor for the lower affinity of TEM8 towards PA compared with CMG2. Because of its high affinity for PA and low expression in normal tissues, an isolated extracellular vWA domain of the L56A TEM8 variant may serve as a potent antitoxin and a potential therapeutic treatment for anthrax infection. Moreover, as TEM8 is often over-expressed in tumor cells, our TEM8 crystal structure may provide new insights into how to design PA mutants that preferentially target tumor cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selection of anthrax toxin protective antigen variants that discriminate between the cellular receptors TEM8 and CMG2 and achieve targeting of tumor cells.J Biol Chem. 2007 Mar 30;282(13):9834-9845. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M611142200. Epub 2007 Jan 24. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17251181 Free PMC article.
-
The receptors that mediate the direct lethality of anthrax toxin.Toxins (Basel). 2012 Dec 27;5(1):1-8. doi: 10.3390/toxins5010001. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23271637 Free PMC article.
-
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the vWA domain of human anthrax toxin receptor 1.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011 Jan 1;67(Pt 1):64-7. doi: 10.1107/S1744309110043770. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011. PMID: 21206026 Free PMC article.
-
Anthrax toxin: receptor binding, internalization, pore formation, and translocation.Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:243-65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.103004.142728. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17335404 Review.
-
Interactions between anthrax toxin receptors and protective antigen.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005 Feb;8(1):106-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.12.005. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15694864 Review.
Cited by
-
A protective antigen mutation increases the pH threshold of anthrax toxin receptor 2-mediated pore formation.Biochemistry. 2014 Apr 8;53(13):2166-71. doi: 10.1021/bi5000756. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 24641616 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Protein-Protein Interfaces through a Protein Contact Network Approach.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015 Oct 30;3:170. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2015.00170. eCollection 2015. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26579512 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers Discovery for Colorectal Cancer: A Review on Tumor Endothelial Markers as Perspective Candidates.Dis Markers. 2016;2016:4912405. doi: 10.1155/2016/4912405. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Dis Markers. 2016. PMID: 27965519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AB Toxins as High-Affinity Ligands for Cell Targeting in Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 7;24(13):11227. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311227. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-Linked Glycosylation on Anthrax Toxin Receptor 1 Is Essential for Seneca Valley Virus Infection.Viruses. 2021 Apr 28;13(5):769. doi: 10.3390/v13050769. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33924774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moayeri M, Leppla SH. The roles of anthrax toxin in pathogenesis. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004;7:19–24. - PubMed
-
- Collier RJ, Young JA. Anthrax toxin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2003;19:45–70. - PubMed
-
- Beauregard KE, Collier RJ, Swanson JA. Proteolytic activation of receptor-bound anthrax protective antigen on macrophages promotes its internalization. Cell Microbiol. 2000;2:251–258. - PubMed
-
- Melnyk RA, Hewitt KM, Lacy DB, Lin HC, Gessner CR, et al. Structural determinants for the binding of anthrax lethal factor to oligomeric protective antigen. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:1630–1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

