The terminal immunoglobulin-like repeats of LigA and LigB of Leptospira enhance their binding to gelatin binding domain of fibronectin and host cells
- PMID: 20585579
- PMCID: PMC2892007
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011301
The terminal immunoglobulin-like repeats of LigA and LigB of Leptospira enhance their binding to gelatin binding domain of fibronectin and host cells
Abstract
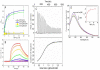
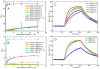
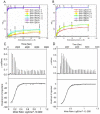
Leptospira spp. are pathogenic spirochetes that cause the zoonotic disease leptospirosis. Leptospiral immunoglobulin (Ig)-like protein B (LigB) contributes to the binding of Leptospira to extracellular matrix proteins such as fibronectin, fibrinogen, laminin, elastin, tropoelastin and collagen. A high-affinity Fn-binding region of LigB has been localized to LigBCen2, which contains the partial 11th and full 12th Ig-like repeats (LigBCen2R) and 47 amino acids of the non-repeat region (LigBCen2NR) of LigB. In this study, the gelatin binding domain of fibronectin was shown to interact with LigBCen2R (K(D) = 1.91+/-0.40 microM). Not only LigBCen2R but also other Ig-like domains of Lig proteins including LigAVar7'-8, LigAVar10, LigAVar11, LigAVar12, LigAVar13, LigBCen7'-8, and LigBCen9 bind to GBD. Interestingly, a large gain in affinity was achieved through an avidity effect, with the terminal domains, 13th (LigA) or 12th (LigB) Ig-like repeat of Lig protein (LigAVar7'-13 and LigBCen7'-12) enhancing binding affinity approximately 51 and 28 fold, respectively, compared to recombinant proteins without this terminal repeat. In addition, the inhibited effect on MDCKs cells can also be promoted by Lig proteins with terminal domains, but these two domains are not required for gelatin binding domain binding and cell adhesion. Interestingly, Lig proteins with the terminal domains could form compact structures with a round shape mediated by multidomain interaction. This is the first report about the interaction of gelatin binding domain of Fn and Lig proteins and provides an example of Lig-gelatin binding domain binding mediating bacterial-host interaction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Patti JM, Allen BL, McGavin MJ, Hook M. MSCRAMM-mediated adherence of microorganisms to host tissues. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994;48:585–617. - PubMed
-
- Potts JR, Campbell ID. Fibronectin structure and assembly. Curr opin cell Biol. 1994;6(5):648–655. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz-Linek U, Hook M, Potts JR. The molecular basis of fibronectin-mediated bacterial adherence to host cells. Mol Microbiol. 2004;52(3):631–641. - PubMed
-
- Joh D, Speziale P, Gurusiddappa S, Manor J, Hook M. Multiple specificities of the staphylococcal and streptococcal fibronectin-binding microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules. Eur J Biochem. 1998;258(2):897–905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

