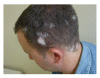
Vitiligo after diphencyprone for alopecia areata
- PMID: 20585597
- PMCID: PMC2879911
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/171265
Vitiligo after diphencyprone for alopecia areata
Abstract
The topical immunotherapy is used to treat alopecia areata and recalcitrant warts since the 1970s. Diphencyprone is a contact sensitizer used to treat dermatological conditions resulting from as altered immunological state, such as extensive alopecia areata, being partially effective and safe. Side effects include local eczema with blistering, regional lymphadenopathy and contact urticaria. Rare adverse effects include an erythema multiforme-like reaction, hyperpigmenttion, hypopigmentation, and vitiligo. We report a 30-year-old, Brazilian male who developed vitiligo lesions following DPCP therapy for alopecia areata.
References
-
- Sittart JAS, Pires MC. Discromias. In: Roca AR, editor. Dermatologia na Prática Médica. São Paulo, Brazil: 2007. pp. 351–368.
-
- Daman LA, Rosenberg EW, Drake L. Treatment of alopecia areata with dinitrochlorobenzene. Archives of Dermatology. 1978;114(7):1036–1038. - PubMed
-
- Happle R, Cebulla K, Echternacht-Happle K. Dinitrochlorobenzene therapy for alopecia areata. Archives of Dermatology. 1978;114(11):1629–1631. - PubMed
-
- Warin AP. Dinitrochlorobenzene in alopecia areata. Lancet. 1979;1(8122):p. 927. - PubMed
-
- Mohan K, Balachandran C, Shenoi S, Rao R, Sripathi H, Prabhu S. Topical dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) for alopecia areata: revisited. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology. 2008;74(4):401–402. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources