Desmosomal component expression in normal, dysplastic, and oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 20585603
- PMCID: PMC2879963
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/649731
Desmosomal component expression in normal, dysplastic, and oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
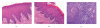
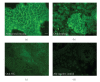
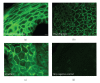
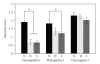
Squamous cell carcinoma (oral SCC) is the most common oral cancer in the U.S., affecting nearly 30,000 Americans each year. Despite recent advances in detection and treatment, there has been little improvement in the five-year survival rate for this devastating disease. Oral cancer may be preceded by premalignant disease that appears histologically as dysplasia. Identification of molecular markers for cellular change would assist in determining the risk of dysplasia progressing to oral squamous cell carcinoma. The goal of this study was to determine if any correlation exists between histological diagnosed dysplasia and OSCC lesions and altered expression of desmosomal cell-cell adhesion molecules in the oral epithelium. Our data showed that oral SCC tissue samples showed decreased immunoreactivity of both desmoplakin and plakophilin-1 proteins compared to normal oral epithelium. Furthermore, significant decrease in desmoplakin immunoreactivity was observed in dysplastic tissue compared to normal oral epithelium. In contrast, the level of desmoglein-1 staining was unchanged between samples however desmoglein-1 was found localized to cell borders in oral SCC samples. These data suggest that changes in expression of desmoplakin and plakophilin-1 may prove to be a useful marker for changes in tissue morphology and provide a tool for identifying pre-neoplastic lesions of the oral cavity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cancer Stem Cell Markers, CD44 and ALDH1, for Assessment of Cancer Risk in OPMDs and Lymph Node Metastasis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Head Neck Pathol. 2022 Jun;16(2):453-465. doi: 10.1007/s12105-021-01384-8. Epub 2021 Oct 16. Head Neck Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34655409 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between immunohistochemical staining of CEACAM1 and clinicopathological findings in oral pre-neoplastic lesions and squamous cell carcinoma.Med Mol Morphol. 2018 Mar;51(1):41-47. doi: 10.1007/s00795-017-0169-4. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Med Mol Morphol. 2018. PMID: 28887602
-
Immunohistochemical staining for desmogleins 1 and 2 in keratinocytic neoplasms with squamous phenotype: actinic keratosis, keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin.Br J Cancer. 1998 Apr;77(8):1275-9. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1998.213. Br J Cancer. 1998. PMID: 9579833 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of toluidine blue in oral premalignant lesions and squamous cell carcinoma: continuing research and implications for clinical practice.Head Neck. 2007 Oct;29(10):948-58. doi: 10.1002/hed.20637. Head Neck. 2007. PMID: 17764090 Review.
-
Lip and Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2021 Oct;35(5):895-911. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2021.05.003. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2021. PMID: 34274176 Review.
Cited by
-
Squamous cell carcinoma of the soft palate associated with autoantibodies to desmoglein 1 and 3.Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013 Oct 31;3(4):55-7. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0304a14. eCollection 2013. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2013. PMID: 24282668 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Serum Epiplakin Might Be a Potential Serodiagnostic Biomarker for Bladder Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 14;13(20):5150. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205150. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680299 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian Plakins, Giant Cytolinkers: Versatile Biological Functions and Roles in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 24;19(4):974. doi: 10.3390/ijms19040974. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29587367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survival, classifications, and desmosomal plaque genes in non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Med Sci. 2013 Jul 10;10(9):1166-73. doi: 10.7150/ijms.5747. Print 2013. Int J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23869193 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule-Actin Crosslinking Factor 1 and Plakins as Therapeutic Drug Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 26;19(2):368. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020368. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29373494 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2007. CA: Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2007;57(1):43–66. - PubMed
-
- Cohen EEW, Baru J, Huo D, et al. Efficacy and safety of treating T4 oral cavity tumors with primary chemoradiotherapy. Head and Neck. 2009;31(8):1013–1021. - PubMed
-
- Rosenthal DI, Mendoza TR, Chambers MS, et al. Measuring head and neck cancer symptom burden: the development and validation of the M. D. Anderson symptom inventory, head and neck module. Head and Neck. 2007;29(10):923–931. - PubMed
-
- Warnakulasuriya S, Reibel J, Bouquot J, Dabelsteen E. Oral epithelial dysplasia classification systems: predictive value, utility, weaknesses and scope for improvement. Journal of Oral Pathology and Medicine. 2008;37(3):127–133. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

