The relBE2Spn toxin-antitoxin system of Streptococcus pneumoniae: role in antibiotic tolerance and functional conservation in clinical isolates
- PMID: 20585658
- PMCID: PMC2890582
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011289
The relBE2Spn toxin-antitoxin system of Streptococcus pneumoniae: role in antibiotic tolerance and functional conservation in clinical isolates
Abstract
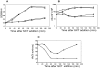
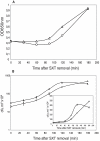
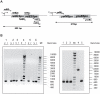
Type II (proteic) chromosomal toxin-antitoxin systems (TAS) are widespread in Bacteria and Archaea but their precise function is known only for a limited number of them. Out of the many TAS described, the relBE family is one of the most abundant, being present in the three first sequenced strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae (D39, TIGR4 and R6). To address the function of the pneumococcal relBE2Spn TAS in the bacterial physiology, we have compared the response of the R6-relBE2Spn wild type strain with that of an isogenic derivative, Delta relB2Spn under different stress conditions such as carbon and amino acid starvation and antibiotic exposure. Differences on viability between the wild type and mutant strains were found only when treatment directly impaired protein synthesis. As a criterion for the permanence of this locus in a variety of clinical strains, we checked whether the relBE2Spn locus was conserved in around 100 pneumococcal strains, including clinical isolates and strains with known genomes. All strains, although having various types of polymorphisms at the vicinity of the TA region, contained a functional relBE2Spn locus and the type of its structure correlated with the multilocus sequence type. Functionality of this TAS was maintained even in cases where severe rearrangements around the relBE2Spn region were found. We conclude that even though the relBE2Spn TAS is not essential for pneumococcus, it may provide additional advantages to the bacteria for colonization and/or infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
The chromosomal relBE2 toxin-antitoxin locus of Streptococcus pneumoniae: characterization and use of a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer assay to detect toxin-antitoxin interaction.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Feb;59(4):1280-96. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05027.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16430700
-
The toxin-antitoxin proteins relBE2Spn of Streptococcus pneumoniae: characterization and association to their DNA target.Proteins. 2012 Jul;80(7):1834-46. doi: 10.1002/prot.24081. Epub 2012 May 8. Proteins. 2012. PMID: 22488579
-
The Streptococcus pneumoniaeyefM-yoeB and relBE Toxin-Antitoxin Operons Participate in Oxidative Stress and Biofilm Formation.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 18;10(9):378. doi: 10.3390/toxins10090378. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30231554 Free PMC article.
-
Toxin-antitoxin genes of the Gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae: so few and yet so many.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012 Dec;76(4):773-91. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00030-12. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23204366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoribonuclease type II toxin-antitoxin systems: functional or selfish?Microbiology (Reading). 2017 Jul;163(7):931-939. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000487. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Microbiology (Reading). 2017. PMID: 28691660 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional validation of putative toxin-antitoxin genes from the Gram-positive pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae: phd-doc is the fourth bona-fide operon.Front Microbiol. 2014 Dec 5;5:677. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00677. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25538695 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the Streptococcus pneumoniae yoeB chromosomal toxin gene causes cell death in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Biotechnol. 2015 Apr 12;15:26. doi: 10.1186/s12896-015-0138-8. BMC Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25887501 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mechanism of programmed cell death in bacteria by toxin-antitoxin systems corrupts peptidoglycan synthesis.PLoS Biol. 2011 Mar;9(3):e1001033. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001033. Epub 2011 Mar 22. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21445328 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Toxin-Antitoxin System Toxins Suppresses Lethality Caused by the Loss of σE in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jul;197(14):2316-24. doi: 10.1128/JB.00079-15. Epub 2015 Apr 27. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25917909 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic regulation of the yefM-yoeB toxin-antitoxin locus of Streptococcus pneumoniae.J Bacteriol. 2011 Sep;193(18):4612-25. doi: 10.1128/JB.05187-11. Epub 2011 Jul 15. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21764929 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Melderen L, Saavedra De Bast M. Bacterial toxin–antitoxin systems: more than selfish entities? PLoS Genetics. 2009;5:e1000437. doi: 1000410.1001371. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gupta A. Killing activity and rescue function of genome-wide toxin-antitoxin loci of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009;290:45–53. - PubMed
-
- Gerdes K, Christensen SK, Lobner-Olesen A. Prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin stress response loci. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3:371–382. - PubMed

