Defective translocation of PKCepsilon in EtOH-induced inhibition of Mg2+ accumulation in rat hepatocytes
- PMID: 20586749
- PMCID: PMC2929311
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01252.x
Defective translocation of PKCepsilon in EtOH-induced inhibition of Mg2+ accumulation in rat hepatocytes
Abstract
Background: Rats chronically fed ethanol for 3 weeks presented a marked decreased in total hepatic Mg(2+) content and required approximately 12 days to restore Mg(2+) homeostasis upon ethanol withdrawal. This study was aimed at investigating the mechanisms responsible for the EtOH-induced delay.
Methods: Hepatocytes from rats fed ethanol for 3 weeks (Lieber-De Carli diet-chronic model), rats re-fed a control diet for varying periods of time following ethanol withdrawal, and age-matched control rats fed a liquid or a pellet diet were used. As acute models, hepatocytes from control animals or HepG2 cells were exposed to varying doses of ethanol in vitro for 8 minutes.
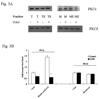
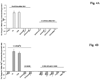
Results: Hepatocytes from ethanol-fed rats presented a marked inhibition of Mg(2+) accumulation and a defective translocation of PKCepsilon to the cell membrane. Upon ethanol withdrawal, 12 days were necessary for PKCepsilon translocation and Mg(2+) accumulation to return to normal levels. Exposure of control hepatocytes or HepG2 cells to a dose of ethanol as low as 0.01% for 8 minutes was already sufficient to inhibit Mg(2+) accumulation and PKCepsilon translocation for more than 60 minutes. Also in this model, recovery of Mg(2+) accumulation was associated with restoration of PKCepsilon translocation. The use of specific antisense in HepG2 cells confirmed the involvement of PKCepsilon in modulating Mg(2+) accumulation.
Conclusions: Translocation of PKCepsilon isoform to the hepatocyte membrane is essential for Mg(2+) accumulation to occur. Both acute and chronic ethanol administrations inhibit Mg(2+) accumulation by specifically altering PKCepsilon translocation to the cell membrane.
Figures








References
-
- Cao G, Thebault S, van der Wijst J, van der Kemp A-M, Lasonder E, Bindels RJM. RACK1 inhibits TRPM6 activity via phosphorylation of the fused alpha-kinase domain. Curr Biol. 2008;18:168–178. - PubMed
-
- Cefaratti C, Romani A. Functional characterization of two distinct Mg2+ extrusion mechanisms in cardiac sarcolemmal vesicles. Mol Cell Biochem. 2007;303:63–72. - PubMed
-
- Csermely P, Fodor P, Somogyi J. The tumor promoter tetradecanoylphorbol-13 acetate elicits the redistribution of heavy metal in subcellular fractions of rabbit thymocytes as measured by plasma emission spectroscopy. Carcinogenesis. 1987;8:1663–1666. - PubMed
-
- Díaz-Guerra MJ, Junco M, Boscá L. Oleic acid promotes changes in the subcellular distribution of protein kinase C in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:23568–23576. - PubMed
-
- Domenicotti C, Paola D, Lamedica A, Ricciarelli R, Chiarpotto E, Marinari UM, Poli G, Melloni E, Pronzato MA. Effects of ethanol metabolism on PKC activity in isolated rat hepatocytes. Chem Biol Interact. 1996;100:155–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

