A hitchhiker's guide to the MADS world of plants
- PMID: 20587009
- PMCID: PMC2911102
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-6-214
A hitchhiker's guide to the MADS world of plants
Abstract
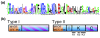
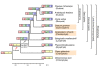
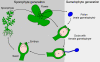
Plant life critically depends on the function of MADS-box genes encoding MADS-domain transcription factors, which are present to a limited extent in nearly all major eukaryotic groups, but constitute a large gene family in land plants. There are two types of MADS-box genes, termed type I and type II, and in plants these groups are distinguished by exon-intron and domain structure, rates of evolution, developmental function and degree of functional redundancy. The type I genes are further subdivided into three groups - M alpha, M beta and M gamma - while the type II genes are subdivided into the MIKCC and MIKC* groups. The functional diversification of MIKCC genes is closely linked to the origin of developmental and morphological novelties in the sporophytic (usually diploid) generation of seed plants, most spectacularly the floral organs and fruits of angiosperms. Functional studies suggest different specializations for the different classes of genes; whereas type I genes may preferentially contribute to female gametophyte, embryo and seed development and MIKC*-group genes to male gametophyte development, the MIKCC-group genes became essential for diverse aspects of sporophyte development. Beyond the usual transcriptional regulation, including feedback and feed-forward loops, various specialized mechanisms have evolved to control the expression of MADS-box genes, such as epigenetic control and regulation by small RNAs. In future, more data from genome projects and reverse genetic studies will allow us to understand the birth, functional diversification and death of members of this dynamic and important family of transcription factors in much more detail.
Figures

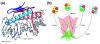
Similar articles
-
Evolution and divergence of the MADS-box gene family based on genome-wide expression analyses.Mol Biol Evol. 2003 Dec;20(12):1963-77. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg216. Epub 2003 Aug 29. Mol Biol Evol. 2003. PMID: 12949148
-
How MIKC* MADS-box genes originated and evidence for their conserved function throughout the evolution of vascular plant gametophytes.Mol Biol Evol. 2012 Jan;29(1):293-302. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr200. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Mol Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 21813465
-
MIKC* MADS-box proteins: conserved regulators of the gametophytic generation of land plants.Mol Biol Evol. 2010 May;27(5):1201-11. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq005. Epub 2010 Jan 15. Mol Biol Evol. 2010. PMID: 20080864
-
MIKC-type MADS-domain proteins: structural modularity, protein interactions and network evolution in land plants.Gene. 2005 Mar 14;347(2):183-98. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.12.014. Epub 2005 Feb 22. Gene. 2005. PMID: 15777618 Review.
-
The major clades of MADS-box genes and their role in the development and evolution of flowering plants.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2003 Dec;29(3):464-89. doi: 10.1016/s1055-7903(03)00207-0. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2003. PMID: 14615187 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Association Study and QTL Mapping Reveal Genomic Loci Associated with Fusarium Ear Rot Resistance in Tropical Maize Germplasm.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Dec 7;6(12):3803-3815. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.034561. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 27742723 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of MIKC-Type MADS-box genes in Chionanthus retusus, an androdioecy plant.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 2;25(1):662. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10569-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38956488 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic containment in vegetatively propagated forest trees: CRISPR disruption of LEAFY function in Eucalyptus gives sterile indeterminate inflorescences and normal juvenile development.Plant Biotechnol J. 2021 Sep;19(9):1743-1755. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13588. Epub 2021 May 4. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33774917 Free PMC article.
-
Selaginella Genome Analysis - Entering the "Homoplasy Heaven" of the MADS World.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Sep 14;3:214. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00214. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 23049534 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of the Mads-Box Transcription Factor Family in Solanum melongena.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):826. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010826. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parenicová L, de Folter S, Kieffer M, Horner DS, Favalli C, Busscher J, Cook HE, Ingram RM, Kater MM, Davies B, Angenent GC, Colombo L. Molecular and phylogenetic analyses of the complete MADS-box transcription factor family in Arabidopsis: new openings to the MADS world. Plant Cell. 2003;15:1538–1551. doi: 10.1105/tpc.011544. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

