Characterization of the human Activin-A receptor type II-like kinase 1 (ACVRL1) promoter and its regulation by Sp1
- PMID: 20587022
- PMCID: PMC2906440
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-51
Characterization of the human Activin-A receptor type II-like kinase 1 (ACVRL1) promoter and its regulation by Sp1
Abstract
Background: Activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) is a Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-beta) receptor type I, mainly expressed in endothelial cells that plays a pivotal role in vascular remodelling and angiogenesis. Mutations in the ALK1 gene (ACVRL1) give rise to Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia, a dominant autosomal vascular dysplasia caused by a haploinsufficiency mechanism. In spite of its patho-physiological relevance, little is known about the transcriptional regulation of ACVRL1. Here, we have studied the different origins of ACVRL1 transcription, we have analyzed in silico its 5'-proximal promoter sequence and we have characterized the role of Sp1 in the transcriptional regulation of ACVRL1.
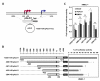
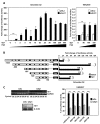
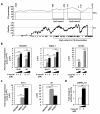
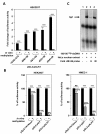
Results: We have performed a 5'Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (5'RACE) of ACVRL1 transcripts, finding two new transcriptional origins, upstream of the one previously described, that give rise to a new exon undiscovered to date. The 5'-proximal promoter region of ACVRL1 (-1,035/+210) was analyzed in silico, finding that it lacks TATA/CAAT boxes, but contains a remarkably high number of GC-rich Sp1 consensus sites. In cells lacking Sp1, ACVRL1 promoter reporters did not present any significant transcriptional activity, whereas increasing concentrations of Sp1 triggered a dose-dependent stimulation of its transcription. Moreover, silencing Sp1 in HEK293T cells resulted in a marked decrease of ACVRL1 transcriptional activity. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated multiple Sp1 binding sites along the proximal promoter region of ACVRL1 in endothelial cells. Furthermore, demethylation of CpG islands, led to an increase in ACVRL1 transcription, whereas in vitro hypermethylation resulted in the abolishment of Sp1-dependent transcriptional activation of ACVRL1.
Conclusions: Our results describe two new transcriptional start sites in ACVRL1 gene, and indicate that Sp1 is a key regulator of ACVRL1 transcription, providing new insights into the molecular mechanisms that contribute to the expression of ACVRL1 gene. Moreover, our data show that the methylation status of CpG islands markedly modulates the Sp1 regulation of ACVRL1 gene transcriptional activity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Counter regulation of ECRG4 gene expression by hypermethylation-dependent inhibition and the Sp1 transcription factor-dependent stimulation of the c2orf40 promoter.Gene. 2017 Dec 15;636:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.08.041. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Gene. 2017. PMID: 28870864
-
Characterization of a proximal Sp1 response element in the mouse Dlk2 gene promoter.BMC Mol Biol. 2011 Dec 20;12:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-12-52. BMC Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 22185379 Free PMC article.
-
The promoter activity of human Mfn2 depends on Sp1 in vascular smooth muscle cells.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Apr 1;94(1):38-47. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs006. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22253285
-
Vascular injury triggers Krüppel-like factor 6 mobilization and cooperation with specificity protein 1 to promote endothelial activation through upregulation of the activin receptor-like kinase 1 gene.Circ Res. 2013 Jan 4;112(1):113-27. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.275586. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23048070 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors and Transcriptional Regulation.In: Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR, editors. C. elegans II. 2nd edition. Cold Spring Harbor (NY): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1997. Chapter 7. In: Riddle DL, Blumenthal T, Meyer BJ, Priess JR, editors. C. elegans II. 2nd edition. Cold Spring Harbor (NY): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1997. Chapter 7. PMID: 21413223 Free Books & Documents. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia with Recurrent Epistaxis, Telangiectasia, Hepatic Arteriovenous Malformation, and a Poorly Developed Middle Cerebral Artery in a Patient with a Novel Mutation in the ACVRL1 Gene.Intern Med. 2025 Feb 1;64(3):477-480. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.3485-24. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 38960693 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modulation as a therapeutic approach for pulmonary arterial hypertension.Exp Mol Med. 2015 Jul 31;47(7):e175. doi: 10.1038/emm.2015.45. Exp Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26228095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 17;7(1):5557. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05705-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28717181 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelin-1 Upregulates Activin Receptor-Like Kinase-1 Expression via Gi/RhoA/Sp-1/Rho Kinase Pathways in Human Pulmonary Arterial Endothelial Cells.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Feb 23;8:648981. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.648981. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33708809 Free PMC article.
-
Splice variants and promoter methylation status of the Bovine Vasa Homology (Bvh) gene may be involved in bull spermatogenesis.BMC Genet. 2013 Jul 1;14:58. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-58. BMC Genet. 2013. PMID: 23815438 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanz-Rodriguez F, Fernandez LA, Zarrabeitia R, Perez-Molino A, Ramirez JR, Coto E, Bernabeu C, Botella LM. Mutation analysis in Spanish patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: deficient endoglin up-regulation in activated monocytes. Clin Chem. 2004;50:2003–2011. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2004.035287. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

