Key role for spinal dorsal horn microglial kinin B1 receptor in early diabetic pain neuropathy
- PMID: 20587056
- PMCID: PMC2913947
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-36
Key role for spinal dorsal horn microglial kinin B1 receptor in early diabetic pain neuropathy
Abstract
Background: The pro-nociceptive kinin B1 receptor (B1R) is upregulated on sensory C-fibres, astrocytes and microglia in the spinal cord of streptozotocin (STZ)-diabetic rat. This study aims at defining the role of microglial kinin B1R in diabetic pain neuropathy.
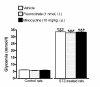
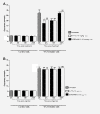
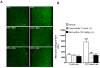
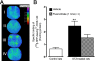
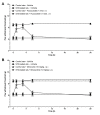
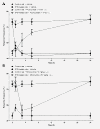
Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats were made diabetic with STZ (65 mg/kg, i.p.), and 4 days later, two specific inhibitors of microglial cells (fluorocitrate, 1 nmol, i.t.; minocycline, 10 mg/kg, i.p.) were administered to assess the impact on thermal hyperalgesia, allodynia and mRNA expression (qRT-PCR) of B1R and pro-inflammatory markers. Spinal B1R binding sites ((125I)-HPP-desArg10-Hoe 140) were also measured by quantitative autoradiography. Inhibition of microglia was confirmed by confocal microscopy with the specific marker Iba-1. Effects of intrathecal and/or systemic administration of B1R agonist (des-Arg9-BK) and antagonists (SSR240612 and R-715) were measured on neuropathic pain manifestations.
Results: STZ-diabetic rats displayed significant tactile and cold allodynia compared with control rats. Intrathecal or peripheral blockade of B1R or inhibition of microglia reversed time-dependently tactile and cold allodynia in diabetic rats without affecting basal values in control rats. Microglia inhibition also abolished thermal hyperalgesia and the enhanced allodynia induced by intrathecal des-Arg9-BK without affecting hyperglycemia in STZ rats. The enhanced mRNA expression (B1R, IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, TRPV1) and Iba-1 immunoreactivity in the STZ spinal cord were normalized by fluorocitrate or minocycline, yet B1R binding sites were reduced by 38%.
Conclusion: The upregulation of kinin B1R in spinal dorsal horn microglia by pro-inflammatory cytokines is proposed as a crucial mechanism in early pain neuropathy in STZ-diabetic rats.
Figures
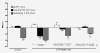


Similar articles
-
Activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin induces functional kinin B(1) receptor in rat spinal cord microglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jan 20;9:16. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-16. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22264228 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular localization of kinin B1 receptor in the spinal cord of streptozotocin-diabetic rats with a fluorescent [Nalpha-Bodipy]-des-Arg9-bradykinin.J Neuroinflammation. 2009 Mar 26;6:11. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-6-11. J Neuroinflammation. 2009. PMID: 19323833 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal Regulatory Interaction between TRPV1 and Kinin B1 Receptor in a Rat Neuropathic Pain Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 27;21(3):821. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030821. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32012798 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of microglial kinin B1 receptor in diabetic pain neuropathy.Exp Neurol. 2012 Apr;234(2):373-81. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.11.032. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Exp Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22154922 Review.
-
Activated microglia in the spinal cord underlies diabetic neuropathic pain.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Apr 5;728:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.057. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24508519 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin induces functional kinin B(1) receptor in rat spinal cord microglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jan 20;9:16. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-16. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22264228 Free PMC article.
-
Pain modality and spinal glia expression by streptozotocin induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats.Lab Anim Res. 2012 Jun;28(2):131-6. doi: 10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.131. Epub 2012 Jun 26. Lab Anim Res. 2012. PMID: 22787487 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine ameliorates cold and mechanical allodynia in a rat model of diabetic neuropathy.J Med Food. 2013 Jun;16(6):511-7. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2012.2648. Epub 2013 Jun 4. J Med Food. 2013. PMID: 23734996 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation in the pathogenesis of microvascular complications in diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012 Dec 21;3:170. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00170. eCollection 2012. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2012. PMID: 23267348 Free PMC article.
-
Olanzapine Attenuates Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation.Korean J Pain. 2015 Jul;28(3):185-92. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2015.28.3.185. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Korean J Pain. 2015. PMID: 26175878 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

