Vacuum-cleaner noise and acute stress responses in female C57BL/6 mice (Mus musculus)
- PMID: 20587160
- PMCID: PMC2877301
Vacuum-cleaner noise and acute stress responses in female C57BL/6 mice (Mus musculus)
Abstract
Audiogenic stress is a well-documented phenomenon in laboratory rodents. Despite the recommendation in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals to consider noise a concern in the animal facility, only a small body of literature empirically addresses the effects of facility noise on laboratory rodents, particularly mice. The objective of this study was to determine whether facility noise generated by a vacuum cleaner induces an acute stress response in a commonly used strain of laboratory mouse under common housing conditions. In each of 2 experiments, 10 young adult, female C57BL/6Cr mice were exposed for 1 h to noise produced by a vacuum cleaner, and 10 control mice were not. In the first experiment, fecal samples were collected to measure concentrations of fecal corticosterone metabolites just before and 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 14, 24, and 32 h after noise exposure. In the second experiment, stress-sensitive behavioral tests were performed 2 d before, immediately after, and 24 h after noise exposure. Physiologic and behavioral measurements indicated that vacuum cleaner noise did not cause an acute stress response in the noise-exposed mice but may have affected the diurnal variation of their corticosterone levels. These findings could contribute to the development of best practices in noise-control protocols for animal facilities.
Figures

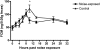


References
-
- Aguas AP, Esaguy N, Grande NR, Castro AP, Castelo Branco NA. 1999. Acceleration of lupus erythematosus-like processes by low-frequency noise in the hybrid NZB/W mouse model. Aviat Space Environ Med 70:A132–A136 - PubMed
-
- Aguas AP, Esaguy N, Grande NR, Castro AP, Castelo Branco NA. 1999. Effect of low-frequency noise exposure on BALB/c mice splenic lymphocytes. Aviat Space Environ Med 70:A128–A131 - PubMed
-
- Anisman H, Hayley S, Kelly O, Borowski T, Merali Z. 2001. Psychogenic, neurogenic, and systemic stressor effects on plasma corticosterone and behavior: mouse strain-dependent outcomes. Behav Neurosci 115:443–454 - PubMed
-
- Anisman H, Zacharko R. 1986. Behavioral and neurochemical consequences associated with stressors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 467:205–225 - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AL, Bell IR. 2007. Effect of noise on microvasculature integrity in laboratory rats. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 46:58–65 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
