Alternative method of oral dosing for rats
- PMID: 20587166
- PMCID: PMC2877307
Alternative method of oral dosing for rats
Abstract
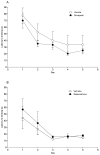
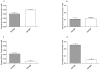
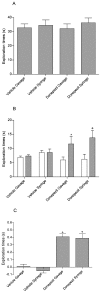
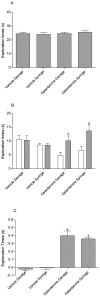
Oral administration of drugs to laboratory rodents typically is achieved by using the gavage technique. Although highly effective, this method occasionally can cause esophageal injury as well as restraint-associated distress, particularly with repeated use. The aim of this study was to assess an alternative oral dosing method that could reduce the distress and morbidity associated with standard gavage techniques. The palatability and pharmacokinetic profile of 2 medicines approved for the treatment of Alzheimer disease, donepezil and galantamine, were investigated in male Lister hooded rats by using a syringe-feeding method and compared with results from traditional gavage administration. In addition, the stimulant nicotine was tested by using the syringe-feeding method in a separate series of experiments. Animals reliably learned to drink voluntarily from the syringe, and latency to drink decreased rapidly. The addition of donepezil, galantamine, or nicotine to sucrose had no apparent effect on the palatability of the solution, although nicotine produced aversive effects that inhibited subsequent voluntary intake. Oral bioavailability was improved by using syringe feeding with donepezil but not galantamine. Both drugs improved cognitive performance in the novel object recognition test, with similar behavioral profiles between the 2 methods of administration. Our results suggest that the syringe-feeding technique is an effective alternative oral dosing method in rats.
Figures



References
-
- Atcha Z, Chen WS, Ong AB, Wong FK, Neo A, Browne ER, Witherington J, Pemberton DJ. 2009. Cognitive enhancing effects of ghrelin receptor agonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 206:415–427 - PubMed
-
- Barnett SW. 2007. Manual of animal technology, 1st ed Hoboken (NJ): Wiley–Blackwell
-
- Beckett AH, Triggs EJ. 1967. Buccal absorption of basic drugs and its application as an in vivo model of passive drug transfer through lipid membranes. J Pharm Pharmacol 19Suppl:31S–41S - PubMed
-
- Bonnichsen M, Dragsted N, Hansen AK. 2005. The welfare impact of gavaging laboratory rats. Anim Welf 14:223–227
-
- Ennaceur A, Delacour J. 1988. A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats I: behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31:47–59 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
