Dogs as sentinels for human infection with Japanese encephalitis virus
- PMID: 20587189
- PMCID: PMC3321903
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1607.091757
Dogs as sentinels for human infection with Japanese encephalitis virus
Abstract
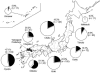
Because serosurveys of Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) among wild animals and pigs may not accurately reflect risk for humans in urban/residential areas, we examined seroprevalence among dogs and cats. We found that JEV-infected mosquitoes have spread throughout Japan and that dogs, but not cats, might be good sentinels for monitoring JEV infection in urban/residential areas.
Figures
References
-
- Arai S, Matsunaga Y, Takasaki T, Tanaka-Taya K, Taniguchi K, Okabe N, et al. ; Vaccine Preventable Diseases Surveillance Program of Japan. Japanese encephalitis: surveillance and elimination effort in Japan from 1982 to 2004. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2008;61:333–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
