Endovascular Pressure Measurements: Validation with a Pulsatile Flow Model and Haemodynamic Assessment of Brain AVMs
- PMID: 20587211
- PMCID: PMC3463287
- DOI: 10.1177/159101990401000401
Endovascular Pressure Measurements: Validation with a Pulsatile Flow Model and Haemodynamic Assessment of Brain AVMs
Abstract
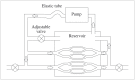
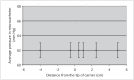
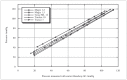
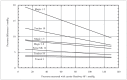
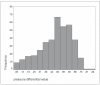
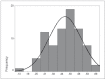
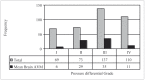
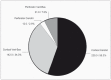
Intravascular pressure measurements for several types of endovascular catheters were obtained in an in vitro model to validate the pressure readings obtained during the interventional procedures of brain AVM embolization. An experimental model was used where the beat rate, flow and pressures were as close as possible to the average human values of interest. It is shown that the corrections increase with the decreasing inner diameter of the catheter used and with increasing vascular pressure. We have also shown that there were no differences between measurements made with the catheter in the direction of flow or against it. An average pressure reading corrections for the various microcatheters to compensate the readings obtained during in vivo monitoring is presented. The haemodynamic assessment of 81 brain AVMs was performed using the endovascular measurement of arterial pressure in 389 feeding arteries during embolization. Mostly, the feeders' arterial median pressure was half the systemic arterial pressure but there was a wide variability of AV shunts in brain AVMs not only from one brain AVM to another but also within the same brain AVM. Measurement of arterial feeder pressure is an inexpensive, quick and accurate tool to evaluate the type of AV shunts within brain AVM.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The endovascular treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations.Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 1998;24:131-214. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6504-1_4. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 1998. PMID: 10050213 Clinical Trial.
-
Accuracy of intravascular microcatheter pressure measurements: an experimental study.Br J Radiol. 1999 May;72(857):448-51. doi: 10.1259/bjr.72.857.10505007. Br J Radiol. 1999. PMID: 10505007
-
Hemodynamic and Anatomical Factors in Arteriovenous Malformation Clinical Presentation: 45 Case Studies.Can J Neurol Sci. 2023 Jan;50(1):37-43. doi: 10.1017/cjn.2021.254. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Can J Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 34747354
-
Endovascular treatment in the multimodality management of brain arteriovenous malformations: report of the Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery Standards and Guidelines Committee.J Neurointerv Surg. 2022 Nov;14(11):1118-1124. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2021-018632. Epub 2022 Apr 12. J Neurointerv Surg. 2022. PMID: 35414599 Review.
-
Ruptured Distal Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA) Aneurysms Associated with Cerebellar Arterial Venous Malformations (AVMs): A Case Series and Review of the Literature Demonstrating the Need for Angiographic Evaluation and Feasibility of Endovascular Treatment.World Neurosurg. 2017 Jan;97:751.e7-751.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.10.081. Epub 2016 Oct 25. World Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 27793767 Review.
Cited by
-
Angiographic factors leading to hemorrhage in AVMs: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurosurg Rev. 2023 Mar 20;46(1):72. doi: 10.1007/s10143-023-01971-z. Neurosurg Rev. 2023. PMID: 36935466
References
-
- Nornes H, Grip A. Haemodynamic aspects of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg. 1980;53:456–464. - PubMed
-
- Hassler W, Steinmetz H. Cerebral haemodynamics in angioma patients: an intraoperative study. J Neurosurg. 1987;67(6):822–831. - PubMed
-
- Barnett GH, Little JR, et al. Cerebral circulation during arteriovenous malformation operation. Neurosurgery. 1987;20:836–842. - PubMed
-
- Leblanc R, Little JR. Haemodynamics of arteriovenous malformations. Clin Neurosurg. 1988;36:299–317. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

