Btk-dependent Rac activation and actin rearrangement following FcepsilonRI aggregation promotes enhanced chemotactic responses of mast cells
- PMID: 20587594
- PMCID: PMC2908047
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.071043
Btk-dependent Rac activation and actin rearrangement following FcepsilonRI aggregation promotes enhanced chemotactic responses of mast cells
Abstract
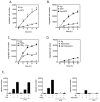
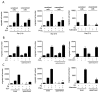
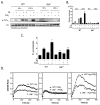
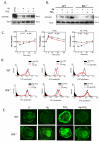
Mast cells infiltrate the sites of inflammation associated with chronic atopic disease and during helminth and bacterial infection. This process requires receptor-mediated cell chemotaxis across a concentration gradient of their chemotactic ligands. In vivo, mast cells are likely to be exposed to several such agents, which can cooperate in a synergistic manner to regulate mast cell homing. Here, we report that chemotaxis of mouse bone-marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs) in response to the chemoattractants stem-cell factor (SCF) and prostaglandin (PG)E(2), is substantially enhanced following antigen-dependent ligation of the high-affinity receptor for IgE (FcεRI). These responses were associated with enhanced activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and downstream activation of the tyrosine protein kinase Btk, with subsequent enhanced phospholipase (PL)Cγ-mediated Ca(2+) mobilization, Rac activation and F-actin rearrangement. Antigen-induced chemotaxis, and the ability of antigen to amplify responses mediated by SCF, adenosine and PGE(2) were suppressed following inhibition of PI3K, and were impaired in BMMCs derived from Btk(-/-) mice. There were corresponding decreases in the PLCγ-mediated Ca(2+) signal, Rac activation and F-actin rearrangement, which, as they are essential for BMMC chemotaxis, accounts for the impaired migration of Btk-deficient cells. Taken together, these data demonstrate that, by regulating signaling pathways that control F-actin rearrangement, Btk is crucial for the ability of antigen to amplify mast-cell chemotactic responses.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Btk plays a crucial role in the amplification of Fc epsilonRI-mediated mast cell activation by kit.J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 2;280(48):40261-70. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506063200. Epub 2005 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16176929
-
Differential use of BTK and PLC in FcεRI- and KIT-mediated mast cell activation: A marginal role of BTK upon KIT activation.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020 Apr;1867(4):118622. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.118622. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31837347
-
Redundant and opposing functions of two tyrosine kinases, Btk and Lyn, in mast cell activation.J Immunol. 2000 Aug 1;165(3):1210-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.3.1210. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10903718
-
Functions of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in mast and B cells.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Mar;65(3):286-90. doi: 10.1002/jlb.65.3.286. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10080529 Review.
-
Signal transduction and chemotaxis in mast cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 May 5;778:11-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.02.057. Epub 2015 May 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 25941081 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stimulus strength determines the BTK-dependence of the SHIP1-deficient phenotype in IgE/antigen-triggered mast cells.Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 19;8(1):15467. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-33769-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30341350 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cell malignancies.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Apr;14(4):219-32. doi: 10.1038/nrc3702. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24658273 Review.
-
IL-33 induces a hyporesponsive phenotype in human and mouse mast cells.J Immunol. 2013 Jan 15;190(2):531-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201576. Epub 2012 Dec 17. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23248261 Free PMC article.
-
Phellinus linteus Grown on Germinated Brown Rice Inhibits IgE-Mediated Allergic Activity through the Suppression of FcεRI-Dependent Signaling Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Nov 29;2019:1485015. doi: 10.1155/2019/1485015. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 31871471 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell biology: introduction and overview.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;716:2-12. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-9533-9_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21713648 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ali H., Cunha-Melo J. R., Saul W. F., Beaven M. A. (1990). Activation of phospholipase C via adenosine receptors provides synergistic signals for secretion in antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. Evidence for a novel adenosine receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 745-753 - PubMed
-
- Brown J. M., Wilson T. M., Metcalfe D. D. (2008). The mast cell and allergic diseases: role in pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Clin. Exp. Allergy 38, 4-18 - PubMed
-
- de Gorter D. J., Beuling E. A., Kersseboom R., Middendorp S., van Gils J. M., Hendriks R. W., Pals S. T., Spaargaren M. (2007). Bruton's tyrosine kinase and phospholipase Cgamma2 mediate chemokine-controlled B cell migration and homing. Immunity 26, 93-104 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

