The HOG pathway dictates the short-term translational response after hyperosmotic shock
- PMID: 20587780
- PMCID: PMC2930000
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E10-01-0006
The HOG pathway dictates the short-term translational response after hyperosmotic shock
Abstract
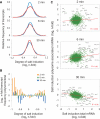
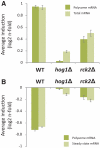
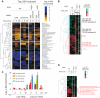
Cellular responses to environmental changes occur on different levels. We investigated the translational response of yeast cells after mild hyperosmotic shock by isolating mRNA associated with multiple ribosomes (polysomes) followed by array analysis. Globally, recruitment of preexisting mRNAs to ribosomes (translational response) is faster than the transcriptional response. Specific functional groups of mRNAs are recruited to ribosomes without any corresponding increase in total mRNA. Among mRNAs under strong translational up-regulation upon shock, transcripts encoding membrane-bound proteins including hexose transporters were enriched. Similarly, numerous mRNAs encoding cytoplasmic ribosomal proteins run counter to the overall trend of down-regulation and are instead translationally mobilized late in the response. Surprisingly, certain transcriptionally induced mRNAs were excluded from ribosomal association after shock. Importantly, we verify, using constructs with intact 5' and 3' untranslated regions, that the observed changes in polysomal mRNA are reflected in protein levels, including cases with only translational up-regulation. Interestingly, the translational regulation of the most highly osmostress-regulated mRNAs was more strongly dependent on the stress-activated protein kinases Hog1 and Rck2 than the transcriptional regulation. Our results show the importance of translational control for fine tuning of the adaptive responses.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stress-dependent coordination of transcriptome and translatome in yeast.PLoS Biol. 2009 May;7(5):e1000105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000105. Epub 2009 May 5. PLoS Biol. 2009. PMID: 19419242 Free PMC article.
-
Rck2 is required for reprogramming of ribosomes during oxidative stress.Mol Biol Cell. 2006 Mar;17(3):1472-82. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-07-0632. Epub 2005 Dec 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2006. PMID: 16381815 Free PMC article.
-
Osmostress-induced gene expression--a model to understand how stress-activated protein kinases (SAPKs) regulate transcription.FEBS J. 2015 Sep;282(17):3275-85. doi: 10.1111/febs.13323. Epub 2015 Jun 10. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25996081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase Hog1 mediates adaptation to G1 checkpoint arrest during arsenite and hyperosmotic stress.Eukaryot Cell. 2008 Aug;7(8):1309-17. doi: 10.1128/EC.00038-08. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Eukaryot Cell. 2008. PMID: 18552285 Free PMC article.
-
Translational regulation in response to stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Yeast. 2019 Jan;36(1):5-21. doi: 10.1002/yea.3349. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Yeast. 2019. PMID: 30019452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction between the transmembrane domains of Sho1 and Opy2 enhances the signaling efficiency of the Hog1 MAP kinase cascade in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 25;14(1):e0211380. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211380. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30682143 Free PMC article.
-
IRES-dependent translated genes in fungi: computational prediction, phylogenetic conservation and functional association.BMC Genomics. 2015 Dec 15;16:1059. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2266-x. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26666532 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast mRNA cap-binding protein Cbc1/Sto1 is necessary for the rapid reprogramming of translation after hyperosmotic shock.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jan;23(1):137-50. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-05-0419. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22072789 Free PMC article.
-
The Hog1 stress-activated protein kinase targets nucleoporins to control mRNA export upon stress.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 14;288(24):17384-98. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.444042. Epub 2013 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23645671 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive post-transcriptional buffering of gene expression in the response to severe oxidative stress in baker's yeast.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 29;9(1):11005. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47424-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31358845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albertsen M., Bellahn I., Kramer R., Waffenschmidt S. Localization and function of the yeast multidrug transporter Tpo1p. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:12820–12825. - PubMed
-
- Alepuz P. M., Jovanovic A., Reiser V., Ammerer G. Stress-induced map kinase Hog1 is part of transcription activation complexes. Mol. Cell. 2001;7:767–777. - PubMed
-
- Asp E., Sunnerhagen P. Mkp1 and Mkp2, two MAPKAP-kinase homologues in Schizosaccharomyces pombe, interact with the MAP kinase Sty1. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2003;268:585–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

