Combination therapy of vaccinia virus infection with human anti-H3 and anti-B5 monoclonal antibodies in a small animal model
- PMID: 20587859
- PMCID: PMC2898516
- DOI: 10.3851/IMP1573
Combination therapy of vaccinia virus infection with human anti-H3 and anti-B5 monoclonal antibodies in a small animal model
Abstract
Background: Treatment of rare severe side effects of vaccinia virus (VACV) immunization in humans is currently very challenging. VACV possesses two immunologically distinct virion forms in vivo - intracellular mature virion (MV, IMV) and extracellular virion (EV, EEV).
Methods: Antibody-mediated therapeutic efficacy was determined against VACV infection in a small animal model of progressive vaccinia. The model consisted of severe combined immunodeficiency mice infected with VACV New York City Board of Health vaccine strain and treated with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs).
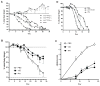
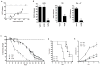
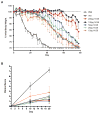
Results: Here, we show that combination therapy with two fully human mAbs against an immunodominant MV antigen, H3 (H3L), and an EV antigen, B5 (B5R), provides significantly better protection against disease and death than either single human monoclonal or human vaccinia immune globulin, the currently licensed therapeutic for side effects of smallpox vaccination.
Conclusions: The preclinical studies validate that this combination of mAbs against H3 and B5 is a promising approach as a poxvirus infection treatment for use in humans.
Figures
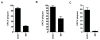


Similar articles
-
Protection of rabbits and immunodeficient mice against lethal poxvirus infections by human monoclonal antibodies.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048706. Epub 2012 Nov 2. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23133652 Free PMC article.
-
Polyclonal antibody cocktails generated using DNA vaccine technology protect in murine models of orthopoxvirus disease.Virol J. 2011 Sep 20;8:441. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-441. Virol J. 2011. PMID: 21933385 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccinia virus extracellular enveloped virion neutralization in vitro and protection in vivo depend on complement.J Virol. 2009 Feb;83(3):1201-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01797-08. Epub 2008 Nov 19. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19019965 Free PMC article.
-
Combinations of polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies to proteins of the outer membranes of the two infectious forms of vaccinia virus protect mice against a lethal respiratory challenge.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(21):13454-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.21.13454-13462.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16227266 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody Recognition of Immunodominant Vaccinia Virus Envelope Proteins.Subcell Biochem. 2017;83:103-126. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46503-6_4. Subcell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28271474 Review.
Cited by
-
Serro 2 Virus Highlights the Fundamental Genomic and Biological Features of a Natural Vaccinia Virus Infecting Humans.Viruses. 2016 Dec 10;8(12):328. doi: 10.3390/v8120328. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27973399 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of mpox M1R and B6R monoclonal and bispecific antibodies that efficiently neutralize authentic mpox virus.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024 Dec;13(1):2401931. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2024.2401931. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024. PMID: 39233480 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced efficacy of cidofovir combined with vaccinia immune globulin in treating progressive cutaneous vaccinia virus infections in immunosuppressed hairless mice.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Jan;59(1):520-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.04289-14. Epub 2014 Nov 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25385098 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of murine antibody responses to vaccinia virus envelope protein A14 reveals an immunodominant antigen lacking of effective neutralization targets.Virology. 2018 May;518:284-292. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2018.03.005. Epub 2018 Mar 17. Virology. 2018. PMID: 29558682 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Human Anti-Poxvirus Monoclonal Antibodies Are Generated from Rare Memory B Cells Isolated by Multicolor Antigen Tetramers.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jul 6;10(7):1084. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10071084. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35891248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Henderson DA, Inglesby TV, Bartlett JG, Ascher MS, Eitzen E, Jahrling PB, Hauer J, Layton M, McDade J, Osterholm MT, O’Toole T, Parker G, Perl T, Russell PK, Tonat K. Smallpox as a biological weapon: medical and public health management. Working Group on Civilian Biodefense. Jama. 1999;281:2127–2137. - PubMed
-
- Fenner F, Henderson DA, Arita I, Jezek Z, Ladnyi ID. Smallpox and its eradication. World Health Organization; Geneva: 1988.
-
- NIAID. NIAID Category A, B & C Priority Pathogens. Edited by Editor|. Year|; p.^pp. Pages|. City|: Publisher|.
-
- NIAID. NIAID High Priority Biodefense Products. 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

