The function of classical and alternative non-homologous end-joining pathways in the fusion of dysfunctional telomeres
- PMID: 20588252
- PMCID: PMC2928694
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.142
The function of classical and alternative non-homologous end-joining pathways in the fusion of dysfunctional telomeres
Abstract
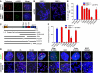
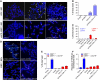
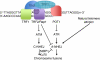
Repair of DNA double-stranded breaks (DSBs) is crucial for the maintenance of genome stability. DSBs are repaired by either error prone non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) or error-free homologous recombination. NHEJ precedes either by a classic, Lig4-dependent process (C-NHEJ) or an alternative, Lig4-independent one (A-NHEJ). Dysfunctional telomeres arising either through natural attrition due to telomerase deficiency or by removal of telomere-binding proteins are recognized as DSBs. In this report, we studied which end-joining pathways are required to join dysfunctional telomeres. In agreement with earlier studies, depletion of Trf2 resulted in end-to-end chromosome fusions mediated by the C-NHEJ pathway. In contrast, removal of Tpp1-Pot1a/b initiated robust chromosome fusions that are mediated by A-NHEJ. C-NHEJ is also dispensable for the fusion of naturally shortened telomeres. Our results reveal that telomeres engage distinct DNA repair pathways depending on how they are rendered dysfunctional, and that A-NHEJ is a major pathway to process dysfunctional telomeres.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Adams MM, Wang B, Xia Z, Morales JC, Lu X, Donehower LA, Bochar DA, Elledge SJ, Carpenter PB (2005) 53BP1 oligomerization is independent of its methylation by PRMT1. Cell Cycle 4: 1854–1861 - PubMed
-
- Artandi SE, Chang S, Lee SL, Alson S, Gottlieb GJ, Chin L, DePinho RA (2000) Telomere dysfunction promotes non-reciprocal translocations and epithelial cancers in mice. Nature 406: 641–645 - PubMed
-
- Audebert M, Salles B, Calsou P (2004) Involvement of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and XRCC1/DNA ligase III in an alternative route for DNA double-strand breaks rejoining. J Biol Chem 279: 55117–55126 - PubMed
-
- Bae NS, Baumann P (2007) A RAP1/TRF2 complex inhibits nonhomologous end-joining at human telomeric DNA ends. Mol Cell 26: 323–334 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

