Therapeutics of diabetes mellitus: focus on insulin analogues and insulin pumps
- PMID: 20589066
- PMCID: PMC2877202
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/178372
Therapeutics of diabetes mellitus: focus on insulin analogues and insulin pumps
Abstract
Aim: Inadequately controlled diabetes accounts for chronic complications and increases mortality. Its therapeutic management aims in normal HbA1C, prandial and postprandial glucose levels. This review discusses diabetes management focusing on the latest insulin analogues, alternative insulin delivery systems and the artificial pancreas.
Results: Intensive insulin therapy with multiple daily injections (MDI) allows better imitation of the physiological rhythm of insulin secretion. Longer-acting, basal insulin analogues provide concomitant improvements in safety, efficacy and variability of glycaemic control, followed by low risks of hypoglycaemia. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) provides long-term glycaemic control especially in type 1 diabetic patients, while reducing hypoglycaemic episodes and glycaemic variability. Continuous subcutaneous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems provide information on postprandial glucose excursions and nocturnal hypo- and/or hyperglycemias. This information enhances treatment options, provides a useful tool for self-monitoring and allows safer achievement of treatment targets. In the absence of a cure-like pancreas or islets transplants, artificial "closed-loop" systems mimicking the pancreatic activity have been also developed.
Conclusions: Individualized treatment plans for insulin initiation and administration mode are critical in achieving target glycaemic levels. Progress in these fields is expected to facilitate and improve the quality of life of diabetic patients.
Figures
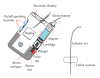
References
-
- Brunton S. Beyond glycemic control: treating the entire type 2 diabetes disorder. Postgraduate Medicine. 2009;121(5):68–81. - PubMed
-
- Cobble ME, Peters AL. Clinical practice in type 2 diabetes: after metformin and lifestyle, then what? The Journal of Family Practice. 2009;58(supplement 11):S7–S14. - PubMed
-
- Philippe J, Raccah D. Treating type 2 diabetes: how safe are current therapeutic agents? International Journal of Clinical Practice. 2009;63(2):321–332. - PubMed
-
- United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33) Lancet. 1998;352:837–853. - PubMed
-
- Selvin E, Wattanakit K, Steffes MW, Coresh J, Sharrett AR. HbA1c and peripheral arterial disease in diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(4):877–882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
