Applying graphics processor units to Monte Carlo dose calculation in radiation therapy
- PMID: 20589122
- PMCID: PMC2884304
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-6203.62198
Applying graphics processor units to Monte Carlo dose calculation in radiation therapy
Abstract
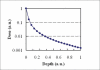
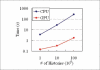
We investigate the potential in using of using a graphics processor unit (GPU) for Monte-Carlo (MC)-based radiation dose calculations. The percent depth dose (PDD) of photons in a medium with known absorption and scattering coefficients is computed using a MC simulation running on both a standard CPU and a GPU. We demonstrate that the GPU's capability for massive parallel processing provides a significant acceleration in the MC calculation, and offers a significant advantage for distributed stochastic simulations on a single computer. Harnessing this potential of GPUs will help in the early adoption of MC for routine planning in a clinical environment.
Keywords: Graphics processor unit; Monte Carlo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chetty IJ, Curran B, Cygler JE, DeMarco JJ, Ezzell G, Faddegon BA, et al. Report of the AAPM Task Group No.105: Issues associated with clinical implementation of Monte Carlo-based photon and electron external beam treatment planning. Med Phys. 2007;34:4818. - PubMed
-
- Dogan N, Siebers JV, Keall PJ, Lerma F, Wu Y, Fatyga M, et al. Improving IMRT dose accuracy via deliverable Monte Carlo optimization for the treatment of head and neck cancer patients. Med Phys. 2006;33:4033–43. - PubMed
-
- Lovelock DM, Chui CS, Mohan R. A Monte Carlo model of photon beams used in radiation therapy. Med Phys. 1995;22:1387–94. - PubMed
-
- Stabin MG, Konijnenberg M, Knapp FF, Jr, Spencer RH. Monte Carlo modeling of radiation dose distributions in intravascular radiation therapy. Med Phys. 2000;27:1086–92. - PubMed
-
- Nelson WR, Hirayama H, Rogers DW. Standford: Standford Linear Accelerator Center; 1985.