Manganese modulation of MAPK pathways: effects on upstream mitogen activated protein kinase kinases and mitogen activated kinase phosphatase-1 in microglial cells
- PMID: 20589745
- PMCID: PMC2995008
- DOI: 10.1002/jat.1552
Manganese modulation of MAPK pathways: effects on upstream mitogen activated protein kinase kinases and mitogen activated kinase phosphatase-1 in microglial cells
Abstract
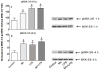
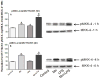
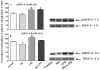
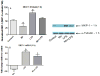
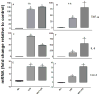
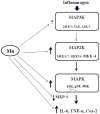
Multiple studies demonstrate that manganese (Mn) exposure potentiates inflammatory mediator output from activated glia; this increased output is associated with enhanced mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK: p38, ERK and JNK) activity. We hypothesized that Mn activates MAPK by activating the kinases upstream of MAPK, i.e. MKK-3/6, MKK-1/2 and MKK-4 (responsible for activation of p38, ERK, and JNK, respectively), and/or by inhibiting a major phosphatase responsible for MAPK inactivation, MKP-1. Exposure of N9 microglia to Mn (250 µm), LPS (100 ng ml⁻¹) or Mn + LPS increased MKK-3/6 and MKK-4 activity at 1 h; the effect of Mn + LPS on MKK-4 activation was greater than the rest. At 4 h, Mn, LPS, and Mn + LPS increased MKK-3/6 and MKK-1/2 phosphorylation, whereas MKK-4 was activated only by Mn and Mn + LPS. Besides activating MKK-4 via Ser257/Thr261 phosphorylation, Mn (4 h) prevented MKK-4's phosphorylation on Ser80, which negatively regulates MKK-4 activity. Exposure to Mn or Mn + LPS (1 h) decreased both mRNA and protein expression of MKP-1, the negative MAPK regulator. In addition, we observed that at 4 h, but not at 1 h, a time point coinciding with increased MAPK activity, Mn + LPS markedly increased TNF-α, IL-6 and Cox-2 mRNA, suggesting a delayed effect. The fact that all three major groups of MKKs, MKK-1/2, MKK-3/6 and MKK-4, are activated by Mn suggests that Mn-induced activation of MAPK occurs via traditional mechanisms, which perhaps involve the MAPKs furthest upstream, MKKKs (MAP3Ks). In addition, for all MKKs, Mn-induced activation was persistent at least for 4 h, indicating a long-term effect.
Copyright © 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
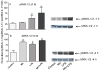
Similar articles
-
Manganese-induced potentiation of in vitro proinflammatory cytokine production by activated microglial cells is associated with persistent activation of p38 MAPK.Toxicol In Vitro. 2008 Feb;22(1):18-27. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Jul 21. Toxicol In Vitro. 2008. PMID: 17845838 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB regulate Helicobacter pylori-mediated interleukin-8 release from macrophages.Biochem J. 2002 Nov 15;368(Pt 1):121-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020555. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12150710 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone suppresses monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production via mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 dependent inhibition of Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in activated rat microglia.J Neurochem. 2007 Aug;102(3):667-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04535.x. Epub 2007 Apr 2. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17403137
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 negatively regulates the expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and cyclooxygenase-2 in A549 human lung epithelial cells.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Apr;333(1):310-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.157438. Epub 2010 Jan 20. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20089808
-
Regulation of JNK and p38 MAPK in the immune system: signal integration, propagation and termination.Cytokine. 2009 Dec;48(3):161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2009.08.002. Epub 2009 Sep 8. Cytokine. 2009. PMID: 19740675 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Manganese and the Insulin-IGF Signaling Network in Huntington's Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;18:113-142. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-60189-2_6. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28889265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Manganese-induced neurotoxicity: a review of its behavioral consequences and neuroprotective strategies".BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016 Nov 4;17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s40360-016-0099-0. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27814772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotoxicity mechanisms of manganese in the central nervous system.Adv Neurotoxicol. 2021;5:215-238. doi: 10.1016/bs.ant.2020.11.003. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Adv Neurotoxicol. 2021. PMID: 34263091 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Microglia amplify inflammatory activation of astrocytes in manganese neurotoxicity.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 May 5;14(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0871-0. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28476157 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Activation of Microglia and Astrocytes in Manganese Neurotoxicity.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;18:159-181. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-60189-2_8. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28889267 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bae JH, Jang BC, Suh SI, Ha E, Baik HH, Kim SS, Lee MY, Shin DH. Manganese induces inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression via activation of both MAP kinase and PI3K/Akt pathways in BV2 microglial cells. Neurosci Lett. 2006;398(1–2):151–4. - PubMed
-
- Barhoumi R, Faske J, Liu X, Tjalkens RB. Manganese potentiates lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of NOS2 in C6 glioma cells through mitochondrial–dependent activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004;122(2):167–79. - PubMed
-
- Bhat NR, Zhang P, Lee JC, Hogan EL. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 subgroups of mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression in endotoxin-stimulated primary glial cultures. J Neurosci. 1998;18(5):1633–41. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

