Synaptic and nonsynaptic localization of protocadherin-gammaC5 in the rat brain
- PMID: 20589908
- PMCID: PMC3209968
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22390
Synaptic and nonsynaptic localization of protocadherin-gammaC5 in the rat brain
Abstract
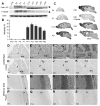
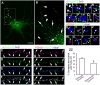
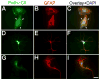
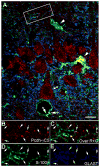
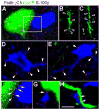
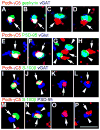
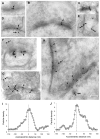
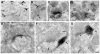
It has been proposed that gamma-protocadherins (Pcdh-gammas) are involved in the establishment of specific patterns of neuronal connectivity. Contrary to the other Pcdh-gammas, which are expressed in the embryo, Pcdh-gammaC5 is expressed postnatally in the brain, coinciding with the peak of synaptogenesis. We have developed an antibody specific for Pcdh-gammaC5 to study the expression and localization of Pcdh-gammaC5 in brain. Pcdh-gammaC5 is highly expressed in the olfactory bulb, corpus striatum, dentate gyrus, CA1 region of the hippocampus, layers I and II of the cerebral cortex, and molecular layer of the cerebellum. Pcdh-gammaC5 is expressed in both neurons and astrocytes. In hippocampal neuronal cultures, and in the absence of astrocytes, a significant percentage of synapses, more GABAergic than glutamatergic, have associated Pcdh-gammaC5 clusters. Some GABAergic axons show Pcdh-gammaC5 in the majority of their synapses. Nevertheless, many Pcdh-gammaC5 clusters are not associated with synapses. In the brain, significant numbers of Pcdh-gammaC5 clusters are located at contact points between neurons and astrocytes. Electron microscopic immunocytochemistry of the rat brain shows that 1) Pcdh-gammaC5 is present in some GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses both pre- and postsynaptically; 2) Pcdh-gammaC5 is also extrasynaptically localized in membranes and in cytoplasmic organelles of neurons and astrocytes; and 3) Pcdh-gammaC5 is also localized in perisynaptic astrocyte processes. The results support the notions that 1) Pcdh-gammaC5 plays a role in synaptic specificity and/or synaptic maturation and 2) Pcdh-gammaC5 is involved in neuron-neuron synaptic interactions and in neuron-astrocyte interactions, including perisynaptic neuron-astrocyte interactions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular and functional interaction between protocadherin-γC5 and GABAA receptors.J Neurosci. 2012 Aug 22;32(34):11780-97. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0969-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22915120 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of protocadherin-γC4 protein in the rat brain.J Comp Neurol. 2020 Apr 1;528(5):840-864. doi: 10.1002/cne.24783. Epub 2019 Nov 6. J Comp Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31609469 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Adhesion Molecule Pcdh-γC5 Mediates Synaptic Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease.J Neurosci. 2017 Sep 20;37(38):9259-9268. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1051-17.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 21. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28842416 Free PMC article.
-
Clustered protocadherin family.Dev Growth Differ. 2008 Jun;50 Suppl 1:S131-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-169X.2008.00991.x. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Dev Growth Differ. 2008. PMID: 18430161 Review.
-
The role and expression of the protocadherin-alpha clusters in the CNS.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006 Jun;16(3):336-42. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2006.05.003. Epub 2006 May 11. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16697637 Review.
Cited by
-
Olfactory receptor genes cooperate with protocadherin genes in human extreme obesity.Genes Nutr. 2015 Jul;10(4):465. doi: 10.1007/s12263-015-0465-3. Epub 2015 May 6. Genes Nutr. 2015. PMID: 25943692 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and functional interaction between protocadherin-γC5 and GABAA receptors.J Neurosci. 2012 Aug 22;32(34):11780-97. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0969-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22915120 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-synapse structural plasticity.Neural Plast. 2014;2014:232105. doi: 10.1155/2014/232105. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Neural Plast. 2014. PMID: 24511394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The female epilepsy protein PCDH19 is a new GABAAR-binding partner that regulates GABAergic transmission as well as migration and morphological maturation of hippocampal neurons.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Mar 15;27(6):1027-1038. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy019. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29360992 Free PMC article.
-
Specification of synaptic connectivity by cell surface interactions.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016 Jan;17(1):22-35. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2015.3. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26656254 Review.
References
-
- Altman J. Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. II. Phases in the maturation of Purkinje cells and of the molecular layer. J Comp Neurol. 1972;145:399–463. - PubMed
-
- Blank M, Triana-Baltzer GB, Richards CS, Berg DK. Alpha-protocadherins are presynaptic and axonal in nicotinic pathways. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004;26:530–543. - PubMed
-
- Charych EI, Yu W, Li R, Serwanski DR, Miralles CP, Li X, Yang BY, Pinal N, Walikonis R, De Blas AL. A four PDZ domain-containing splice variant form of GRIP1 is localized in GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses in the brain. J Biol Chem. 2004a;279:38978–38990. - PubMed
-
- Charych EI, Yu W, Miralles CP, Serwanski DR, Li X, Rubio M, De Blas AL. The brefeldin A-inhibited GDP/GTP exchange factor 2, a protein involved in vesicular trafficking, interacts with the beta subunits of the GABA receptors. J Neurochem. 2004b;90:173–189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

