Stochastic mechanisms of cell fate specification that yield random or robust outcomes
- PMID: 20590453
- PMCID: PMC3025287
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100109-104113
Stochastic mechanisms of cell fate specification that yield random or robust outcomes
Abstract
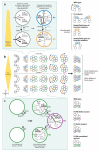
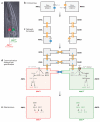
Although cell fate specification is tightly controlled to yield highly reproducible results and avoid extreme variation, developmental programs often incorporate stochastic mechanisms to diversify cell types. Stochastic specification phenomena are observed in a wide range of species and an assorted set of developmental contexts. In bacteria, stochastic mechanisms are utilized to generate transient subpopulations capable of surviving adverse environmental conditions. In vertebrate, insect, and worm nervous systems, stochastic fate choices are used to increase the repertoire of sensory and motor neuron subtypes. Random fate choices are also integrated into developmental programs controlling organogenesis. Although stochastic decisions can be maintained to produce a mosaic of fates within a population of cells, they can also be compensated for or directed to yield robust and reproducible outcomes.
Figures

References
-
- Balaban NQ, Merrin J, Chait R, Kowalik L, Leibler S. Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science. 2004;305:1622–25. - PubMed
-
- Bell ML, Earl JB, Britt SG. Two types of Drosophila R7 photoreceptor cells are arranged randomly: a model for stochastic cell-fate determination. J. Comp. Neurol. 2007;502:75–85. - PubMed
-
- Bigger JW. The bactericidal action of penicillin on Staphylococcus pyogenes. Irish J. Med. Sci. 1944a;227:553–68.
-
- Bigger JW. Treatment of staphylococcal infections with penicillin by intermittent sterilisation. Lancet. 1944b:497–500.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

