Regulation of Fas receptor/Fas-associated protein with death domain apoptotic complex and associated signalling systems by cannabinoid receptors in the mouse brain
- PMID: 20590568
- PMCID: PMC2931564
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00710.x
Regulation of Fas receptor/Fas-associated protein with death domain apoptotic complex and associated signalling systems by cannabinoid receptors in the mouse brain
Abstract
Background and purpose: Natural and synthetic cannabinoids (CBs) induce deleterious or beneficial actions on neuronal survival. The Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) promotes apoptosis, and its phosphorylated form (p-FADD) mediates non-apoptotic actions. The regulation of Fas/FADD, mitochondrial apoptotic proteins and other pathways by CB receptors was investigated in the mouse brain.
Experimental approach: Wild-type, CB(1) and CB(2) receptor knock-out (KO) mice were used to assess differences in receptor genotypes. CD1 mice were used to evaluate the effects of CB drugs on canonical apoptotic pathways and associated signalling systems. Target proteins were quantified by Western blot analysis.
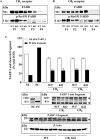
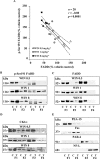
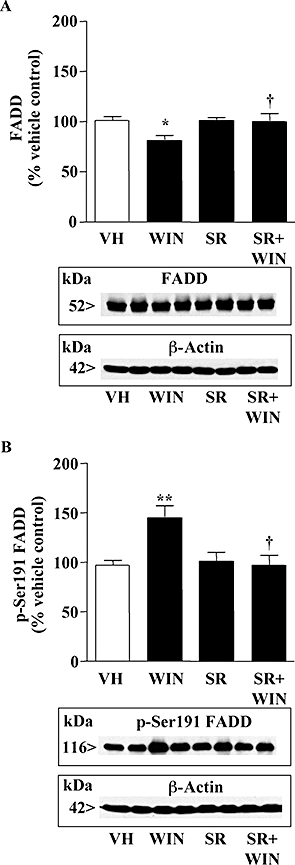
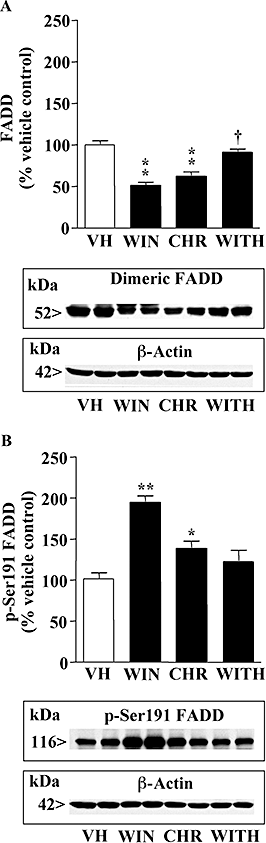
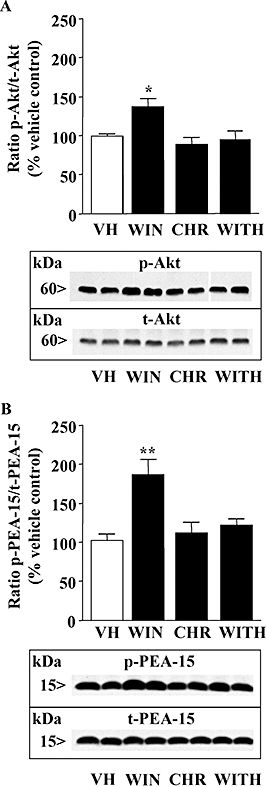
Key results: In brain regions of CB(1) receptor KO mice, Fas/FADD was reduced, but p-Ser191 FADD and the p-FADD/FADD ratio were increased. In CB(2) receptor KO mice, Fas/FADD was increased, but the p-FADD/FADD ratio was not modified. In mutant mice, cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose)-polymerase (PARP) did not indicate alterations in brain cell death. In CD1 mice, acute WIN55212-2 (CB(1) receptor agonist), but not JWH133 (CB(2) receptor agonist), inversely modulated brain FADD and p-FADD. Chronic WIN55212-2 induced FADD down-regulation and p-FADD up-regulation. Acute and chronic WIN55212-2 did not alter mitochondrial proteins or PARP cleavage. Acute, but not chronic, WIN55212-2 stimulated activation of anti-apoptotic (ERK, Akt) and pro-apoptotic (JNK, p38 kinase) pathways.
Conclusions and implications: CB(1) receptors appear to exert a modest tonic activation of Fas/FADD complexes in brain. However, chronic CB(1) receptor stimulation decreased pro-apoptotic FADD and increased non-apoptotic p-FADD. The multifunctional protein FADD could participate in the mechanisms of neuroprotection induced by CBs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Regulation of cannabinoid CB2 receptor constitutive activity in vivo: repeated treatments with inverse agonists reverse the acute activation of JNK and associated apoptotic signaling in mouse brain.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Mar;234(6):925-941. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4537-5. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28127623
-
The CB1/CB2 receptor agonist WIN-55,212-2 reduces viability of human Kaposi's sarcoma cells in vitro.Eur J Pharmacol. 2009 Aug 15;616(1-3):16-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.06.004. Epub 2009 Jun 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19539619
-
Chronic treatment with selective I2-imidazoline receptor ligands decreases the content of pro-apoptotic markers in rat brain.J Psychopharmacol. 2013 Feb;27(2):123-34. doi: 10.1177/0269881112450785. Epub 2012 Jun 20. J Psychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22719017
-
Cannabinoids in the treatment of cancer.Cancer Lett. 2009 Nov 18;285(1):6-12. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.04.005. Epub 2009 May 12. Cancer Lett. 2009. PMID: 19442435 Review.
-
Cellular Dynamics of Fas-Associated Death Domain in the Regulation of Cancer and Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 12;25(6):3228. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063228. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542202 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased proliferation of adult hippocampal stem cells during cocaine withdrawal: possible role of the cell fate regulator FADD.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 Oct;36(11):2303-17. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.119. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21796105 Free PMC article.
-
Cholecystokinin octapeptide antagonizes apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.Neural Regen Res. 2014 Jul 15;9(14):1402-8. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.137596. Neural Regen Res. 2014. PMID: 25221599 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cannabinoid CB2 receptor constitutive activity in vivo: repeated treatments with inverse agonists reverse the acute activation of JNK and associated apoptotic signaling in mouse brain.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017 Mar;234(6):925-941. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4537-5. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28127623
-
Imaging and Genetic Tools for the Investigation of the Endocannabinoid System in the CNS.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 31;24(21):15829. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115829. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The synthetic cannabinoid R(+)WIN55,212-2 augments interferon-β expression via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 20;287(30):25440-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.371757. Epub 2012 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22654113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguado T, Romero E, Monory K, Palazuelos J, Sendtner M, Marsicano G, et al. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor mediates excitotoxicity-induced neural progenitor proliferation and neurogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:23892–23898. - PubMed
-
- Alappat EC, Feig C, Boyerinas B, Volkland J, Samuels M, Murmann AE, et al. Phosphorylation of FADD at serine 194 by CKIα regulates its nonapoptotic activities. Mol Cell. 2005;19:321–332. - PubMed
-
- Álvaro-Bartolomé M, Esteban S, Valverde O, García-Sevilla JA. Regulation of pro-apoptotic Fas/FADD receptor complex in brain regions of CB1 receptor-deficient mice. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2008;18(Suppl. 4):S230–S231.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

