A role for L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol and GPR55 in the modulation of migration, orientation and polarization of human breast cancer cells
- PMID: 20590578
- PMCID: PMC2931574
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00743.x
A role for L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol and GPR55 in the modulation of migration, orientation and polarization of human breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Increased circulating levels of L-alpha-lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI) are associated with cancer and LPI is a potent, ligand for the G-protein-coupled receptor GPR55. Here we have assessed the modulation of breast cancer cell migration, orientation and polarization by LPI and GPR55.
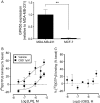
Experimental approach: Quantitative RT-PCR was used to measure GPR55 expression in breast cancer cell lines. Cell migration and invasion were measured using a Boyden chamber chemotaxis assay and Cultrex invasion assay, respectively. Cell polarization and orientation in response to the microenvironment were measured using slides containing nanometric grooves.
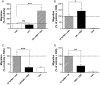
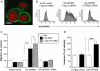
Key results: GPR55 expression was detected in the highly metastatic MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. In these cells, LPI stimulated binding of [(35)S]GTPgammaS to cell membranes (pEC(50) 6.47 +/- 0.45) and significantly enhanced cell chemotaxis towards serum. MCF-7 cells expressed low levels of GPR55 and did not migrate or invade towards serum factors. When GPR55 was over-expressed in MCF-7 cells, serum induced a robust migratory and invasive response, which was further enhanced by LPI and prevented by siRNA to GPR55. The physical microenvironment has been identified as a key factor in determining breast tumour cell metastatic fate. LPI endowed MDA-MB-231 cells with the capacity to detect shallow (40 nm deep) grooved slides and induced marked cancer cell polarization on both flat and grooved surfaces.
Conclusions and implications: LPI and GPR55 play a role in the modulation of migration, orientation and polarization of breast cancer cells in response to the tumour microenvironment.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed T, Shea K, Masters JR, Jones GE, Wells CM. A PAK4-LIMK1 pathway drives prostate cancer cell migration downstream of HGF. Cell Signal. 2008;20:1320–1328. - PubMed
-
- Anavi-Goffer S, Fleischer D, Hurst DP, Lynch DL, Barnett-Norris, Shi S, et al. Helix 8 Leu in the CB1 cannabinoid receptor contributes to selective signal transduction mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:25100–25113. - PubMed
-
- Chen YL, Xu Y. Determination of lysophosphatidic acids by capillary electrophoresis with indirect ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2001;753:355–363. - PubMed
-
- Croft DR, Olson MF. Regulating the conversion between rounded and elongated modes of cancer cell movement. Cancer Cell. 2008;14:349–351. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

