Purinoreceptor-mediated current in myocytes from renal resistance arteries
- PMID: 20590593
- PMCID: PMC2936003
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00714.x
Purinoreceptor-mediated current in myocytes from renal resistance arteries
Abstract
Background and purpose: Ionotropic purinoreceptors (P2X) in renal vascular smooth muscle cells (RVSMCs) are involved in mediating the sympathetic control and paracrine regulation of renal blood flow (RBF). Activation of P2X receptors elevates [Ca(2+)](i) in RVSMCs triggering their contraction, leading to renal vasoconstriction and decrease of RBF. The goal of the present work was to characterize the P2X receptor-mediated ionic current (I(P2X)) and to identify the types of P2X receptors expressed in myocytes isolated from interlobar and arcuate arteries of rat kidney.
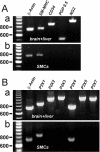
Experimental approach: The expression of P2X receptors in isolated RVSMCs was analysed by reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. I(P2X) and membrane potential were recorded using the amphotericin B-perforated patch method.
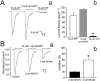
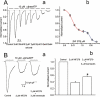
Key results: RT-PCR analysis on single RVSMCs showed the presence of genes encoding P2X1 and P2X4 receptors. Under voltage clamp conditions, the selective P2X receptor agonist alphabeta-methylene ATP (alphabeta-meATP) evoked I(P2X) similar to that induced by ATP. Under current clamp conditions, both ATP and alphabeta-meATP evoked a spike-like membrane depolarization followed by a sustained depolarization, linking P2X receptors in RVSMCs to sympathetic control of renal vascular tone. A selective antagonist of P2X1 receptors, NF279, reduced I(P2X) amplitude by approximately 65% concentration-dependently manner within the nanomolar to sub-micromolar range. The residual current was resistant to micromolar concentrations of NF279, but was inhibited by sub-millimolar to millimolar concentrations of NF279.
Conclusions and implications: Two types of functional P2X receptors, monomeric P2X1 and heteromeric P2X1/4 receptors, are expressed in RVSMCs. Our study has identified important targets for possible pharmacological intervention in the sympathetic control of renal circulation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Ca2+ entry following P2X receptor activation induces IP3 receptor-mediated Ca2+ release in myocytes from small renal arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;162(7):1618-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01169.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21175582 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification of P2X receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells from rat anterior, posterior, and basilar arteries.Pharmacol Rep. 2015 Dec;67(6):1055-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Pharmacol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26481522
-
Lack of run-down of smooth muscle P2X receptor currents recorded with the amphotericin permeabilized patch technique, physiological and pharmacological characterization of the properties of mesenteric artery P2X receptor ion channels.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Dec;131(8):1659-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703744. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11139444 Free PMC article.
-
ATP as a cotransmitter in perivascular sympathetic nerves.J Auton Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;16(6):337-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1996.tb00048.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 9131411 Review.
-
Mechanisms of ATP release and signalling in the blood vessel wall.Cardiovasc Res. 2012 Aug 1;95(3):269-80. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs187. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Cardiovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22678409 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
P2X1 receptor-mediated vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles in angiotensin II-infused hypertensive rats fed a high-salt diet.Hypertension. 2011 Apr;57(4):780-7. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.168955. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Hypertension. 2011. PMID: 21321307 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in vasoconstrictor responses to the endothelium-derived contracting factor uridine adenosine tetraphosphate are region specific in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.Pharmacol Res. 2012 Jan;65(1):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Pharmacol Res. 2012. PMID: 21933714 Free PMC article.
-
The Calcium Signaling Mechanisms in Arterial Smooth Muscle and Endothelial Cells.Compr Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;11(2):1831-1869. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c200030. Compr Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33792900 Free PMC article.
-
Pentosan polysulfate preserves renal microvascular P2X1 receptor reactivity and autoregulatory behavior in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Mar 15;310(6):F456-65. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00110.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26697978 Free PMC article.
-
Purinoceptors, renal microvascular function and hypertension.Physiol Res. 2020 Jul 16;69(3):353-369. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934463. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Physiol Res. 2020. PMID: 32301620 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bo X, Burnstock G. Characterization and autoradiographic localization of [3H] alpha, beta-methylene adenosine 5′-triphosphate binding sites in human urinary bladder. Br J Urol. 1995;76:297–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

