Failure of Bay K 8644 to induce RhoA kinase-dependent calcium sensitization in rabbit blood vessels
- PMID: 20590624
- PMCID: PMC2938805
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00751.x
Failure of Bay K 8644 to induce RhoA kinase-dependent calcium sensitization in rabbit blood vessels
Abstract
Background and purpose: RhoA kinase (ROCK) participates in K(+) depolarization (KCl)-induced Ca(2+) sensitization of contraction. Whether constitutive, depolarization- or Ca(2+)-activated ROCK plays the major role in this signalling system remains to be determined. Here, we determined whether Bay K 8644, a dihydropyridine that promotes Ca(2+) channel clusters to operate in a persistent Ca(2+) influx mode, could cause ROCK-dependent Ca(2+) sensitization.
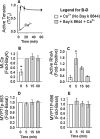
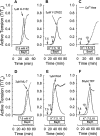
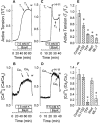
Experimental approach: Renal and femoral artery rings from New Zealand white rabbits were contracted with Bay K 8644. Tissues were frozen and processed to measure active RhoA and ROCK substrate (myosin phosphatase targeting subunit, MYPT1) and myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation, or loaded with fura-2 to measure intracellular free Ca(2+) ([Ca(2+)](i)). Effects of selective inhibitors of contraction were assessed in resting (basal) tissues and those contracted with Bay K 8644.
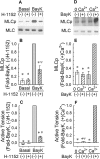
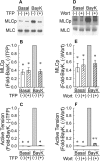
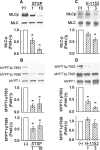
Key results: Bay K 8644 produced strong increases in [Ca(2+)](i), MLC phosphorylation and tension, but not in MYPT1 phosphorylation. ROCK inhibition by H-1152 abolished basal MYPT1-pT853, diminished basal MLC phosphorylation and inhibited Bay K 8644-induced increases in MLC phosphorylation and tension. MLC kinase inhibition by wortmannin abolished Bay K 8644-induced contraction and increase in MLC phosphorylation but did not inhibit basal MYPT1-pT853. H-1152 and wortmannin had no effect on MYPT1-pT696, but 1 microM staurosporine inhibited basal MYPT1-pT853, MYPT1-pT696 and MLC phosphorylation.
Conclusions and implications: These data suggest that the constitutive activities of ROCK and a staurosporine-sensitive kinase regulate basal phosphorylation of MYPT1, which participates along with activation of MLC kinase in determining the strength of contraction induced by the Ca(2+) agonist, Bay K 8644.
Figures



References
-
- Asano M, Nomura Y. Comparison of inhibitory effects of Y-27632, a Rho kinase inhibitor, in strips of small and large mesenteric arteries from spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive Wistar-Kyoto rats. Hypertens Res. 2003;26:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Brown AM, Kunze DL, Yatani A. The agonist effect of dihydropyridines on Ca channels. Nature. 1984;311:570–572. - PubMed
-
- Brozovich FV. Rho signaling: agonist stimulation and depolarization come together. Circ Res. 2003;93:481–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

