Openers of small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels selectively enhance NO-mediated bradykinin vasodilatation in porcine retinal arterioles
- PMID: 20590639
- PMCID: PMC2938820
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00803.x
Openers of small conductance calcium-activated potassium channels selectively enhance NO-mediated bradykinin vasodilatation in porcine retinal arterioles
Abstract
Background and purpose: Small (SK(Ca) or K(Ca)2) and intermediate (IK(Ca) or K(Ca)3.1) conductance calcium-activated potassium channels are involved in regulation of vascular tone and blood pressure. The present study investigated whether NS309 (6,7-dichloro-1H-indole-2,3-dione 3-oxime) and CyPPA (cyclohexyl-[2-(3,5-dimethyl-pyrazol-1-yl)-6-methyl-pyrimidin-4-yl]-amine), which are selective openers of SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels and of SK(Ca)2 and SK(Ca)3 channels, respectively, enhance endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in porcine retinal arterioles.
Experimental approach: In porcine retinal arterioles, SK(Ca)3 and IK(Ca) protein localization was examined by immunolabelling. Endothelial cell calcium was measured by fluorescence imaging. For functional studies, arterioles with internal diameters of 116 +/- 2 microm (n = 276) were mounted in microvascular myographs for isometric tension recordings.
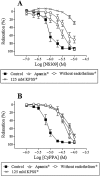
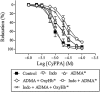
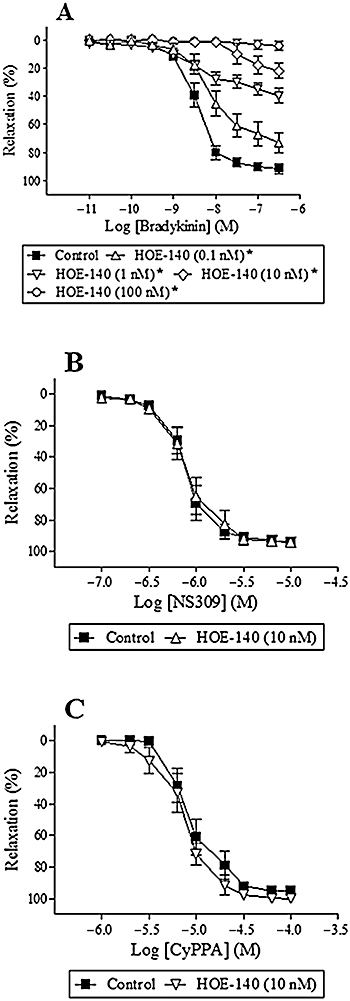
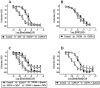
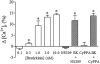
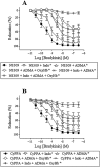
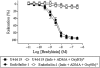
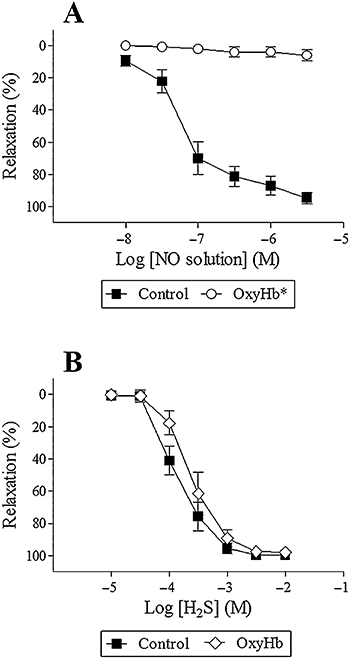
Key results: SK(Ca)3 and IK(Ca) protein was localized in the endothelium. Bradykinin, but not NS309 or CyPPA increased endothelial cell calcium. Pre-incubation with NS309 or CyPPA enhanced bradykinin relaxation without changing endothelial cell calcium. This enhanced relaxation was abolished by blocking SK(Ca) channels with apamin. In the presence of NS309 or CyPPA, mainly inhibition of NO synthase with asymmetric dimethylarginine, but also inhibition of cyclooxygenase with indomethacin, reduced bradykinin relaxation. Bradykinin relaxation was completely abolished by NO synthase and cyclooxygenase inhibition together with a NO scavenger, oxyhaemoglobin.
Conclusions and implications: In porcine retinal arterioles, bradykinin increases endothelial cell calcium leading to activation of SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels. Without altering endothelial cell calcium, NS309 and CyPPA open SK(Ca) channels that enhance NO-mediated bradykinin relaxations. These results imply that opening SK(Ca) channels improves endothelium-dependent relaxation and makes this channel a potential target for treatments aimed at restoring retinal blood flow.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of calcium-activated potassium channels with small conductance in bradykinin-induced vasodilation of porcine retinal arterioles.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Aug;50(8):3819-25. doi: 10.1167/iovs.08-3168. Epub 2009 Feb 28. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19255162
-
Opening of small and intermediate calcium-activated potassium channels induces relaxation mainly mediated by nitric-oxide release in large arteries and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in small arteries from rat.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011 Dec;339(3):842-50. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.179242. Epub 2011 Aug 31. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011. PMID: 21880870
-
NS309 restores EDHF-type relaxation in mesenteric small arteries from type 2 diabetic ZDF rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jan;159(1):154-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00525.x. Epub 2009 Dec 10. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20015296 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-activated potassium channels - a therapeutic target for modulating nitric oxide in cardiovascular disease?Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010 Aug;14(8):825-37. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2010.500616. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2010. PMID: 20560781 Review.
-
Endothelium-derived hyperpolarising factors and associated pathways: a synopsis.Pflugers Arch. 2010 May;459(6):863-79. doi: 10.1007/s00424-010-0817-1. Epub 2010 Apr 11. Pflugers Arch. 2010. PMID: 20383718 Review.
Cited by
-
SKA-31, a novel activator of SK(Ca) and IK(Ca) channels, increases coronary flow in male and female rat hearts.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Feb 1;97(2):339-48. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs326. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23118129 Free PMC article.
-
Kinin B1 receptor and TLR4 interaction in inflammatory response.Inflamm Res. 2024 Sep;73(9):1459-1476. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01909-1. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38965133
-
Tranilast increases vasodilator response to acetylcholine in rat mesenteric resistance arteries through increased EDHF participation.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 3;9(7):e100356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100356. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24992476 Free PMC article.
-
Coronary endothelial dysfunction prevented by small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activator in mice and patients with diabetes.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020 Dec;160(6):e263-e280. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2020.01.078. Epub 2020 Feb 19. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 32199659 Free PMC article.
-
Vasodilatory Effect of Phellinus linteus Extract in Rat Mesenteric Arteries.Molecules. 2020 Jul 10;25(14):3160. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143160. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32664327 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams DJ, Barakeh J, Laskey R, Van Breemen C. Ion channels and regulation of intracellular calcium in vascular endothelial cells. FASEB J. 1989;3:2389–2400. - PubMed
-
- Beauchamp RO, Jr, Bus JS, Popp JA, Boreiko CJ, Andjelkovich DA. A critical review of the literature on hydrogen sulfide toxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1984;13:25–97. - PubMed
-
- Brahler S, Kaistha A, Schmidt VJ, Wolfle SE, Busch C, Kaistha BP, et al. Genetic deficit of SK3 and IK1 channels disrupts the endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor vasodilator pathway and causes hypertension. Circulation. 2009;119:2323–2332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

