A systematic review and meta-analysis of telmisartan versus valsartan in the management of essential hypertension
- PMID: 20591086
- PMCID: PMC8673417
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2010.00287.x
A systematic review and meta-analysis of telmisartan versus valsartan in the management of essential hypertension
Abstract
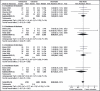
This was a systematic assessment of the efficacy and safety of telmisartan and valsartan for the management of blood pressure (BP) in patients with essential hypertension. The authors reviewed randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs comparing telmisartan and valsartan for the management of essential hypertension in which the participants were followed for at least 6 weeks. When a metaanalysis was possible, included studies were analyzed by Review Manager 5.0 provided by Cochrane Collaboration Group. Statistics were calculated as weight mean differences (WMDs) and relative risk with a random-effect model. A total of 6 RCTs with 3762 patients were included in this metaanalysis. When the authors combined data from all treatment categories as a group, no difference was found between telmisartan and valsartan in reduction of systolic BP and diastolic BP. In subgroup analysis, telmisartan showed a significant benefit on lowering systolic BP and diastolic BP (WMD, -2.88; 95% confidence interval [CI], -5.03 to -0.73; P<0.01; and WMD,-1.73; 95% CI, -2.47 to -0.98; P<0.01; respectively). It was found that telmisartan had a higher rate of management of clinical BP compared with valsartan (relative risk, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.00-1.19; P=0.05). No difference was found in the incidence of adverse events. Telmisartan's BP-lowering capabilities were comparable to those of valsartan in monotherapy. When combined with hydrochlorothiazide, telmisartan was more effective than valsartan. Telmisartan had the same safety in the treatment of essential hypertensive patients in comparison with valsartan.
Copyright 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of renin inhibitors for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 5;4(4):CD007066. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007066.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28379619 Free PMC article.
-
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of beta-1 selective beta blockers for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 10;3(3):CD007451. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007451.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26961574 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-blockers for hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 20;1(1):CD002003. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002003.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28107561 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the angiotensin II receptor blockers telmisartan vs valsartan in combination with hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg once daily for the treatment of hypertension.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2006 Sep;8(9):626-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2006.05411.x. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2006. PMID: 16957424 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
Cited by
-
Scaling up effective treatment of hypertension-A pathfinder for universal health coverage.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2019 Oct;21(10):1442-1449. doi: 10.1111/jch.13655. Epub 2019 Sep 23. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2019. PMID: 31544349 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Hypertension Using Olmesartan Alone or in Combination.Cardiol Ther. 2017 Jun;6(1):13-32. doi: 10.1007/s40119-017-0087-5. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Cardiol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28258390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Effectiveness of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in Patients With Hypertension in Japan - Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Circ Rep. 2020 Sep 18;2(10):576-586. doi: 10.1253/circrep.CR-20-0076. Circ Rep. 2020. PMID: 33693183 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of effects of telmisartan versus valsartan on post-induction hypotension during noncardiac surgery: a prospective observational study.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2024 Jun;77(3):335-344. doi: 10.4097/kja.23658. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 38311886 Free PMC article.
-
Telmisartan alleviates collagen type III glomerulopathy: A case report with literature review.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Dec;20(6):140. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9269. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 33093878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahmouni K, Correia ML, Haynes WG, et al. Obesity‐associated hypertension: new insights into mechanisms. Hypertension. 2005;45:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Burnier M, Maillard M. The comparative pharmacology of angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Blood Press Suppl 2001;10:6–10. - PubMed
-
- Kakuta H, Sudoh K, Sasmata M, et al. Telmisartan has the strongest binding affinity to angiotensin II type I receptor: comparison with other angiotensin II type I receptor blockers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 2005;25:41–46. - PubMed
-
- Wienen W, Entzeroth M, Van Meel JCA, et al. A review on telmisartan: a novel, long‐acting angiotensin II receptor antagonist. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 2002;18:127–156.
-
- Lasko BH, Laplante A, Hebert D, et al. Canadian valsartan study in patients with mild‐to‐moderate hypertension. Blood Press Monit. 2001;6:91–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

