Hydroxyapatite and bFGF Coating of Detachable Coils for Endovascular Occlusion of Experimental Aneurysm
- PMID: 20591225
- PMCID: PMC3553474
- DOI: 10.1177/15910199030090S102
Hydroxyapatite and bFGF Coating of Detachable Coils for Endovascular Occlusion of Experimental Aneurysm
Abstract
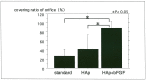
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of hydroxyapatite (HAp) and fibroblast growth factor-basic (bFGF) coating on Guglielmi detachable coils (GDCs) in an experimental aneurysm model. A total of 18 aneurysms were experimentally made in the common carotid arteries of swine. Embolization was done on these aneurysms using standard GDCs and coated GDCs with HAp (GDC-HAp) and with bFGF (GDC-HAp-bFGF). The animals were then killed 14 days after embolization. The development of tissue scarring and coverage the aneurysm's orifice were evaluated macroscopically. No significant difference of volume ratio of the coils exited in each groups. Macroscopically, covering ratio of fibrous membrane at the neck of aneurysms were 88.3 +/- 14.7% in a group with GDC-HAp-bFGF, while it were 26.7 +/- 15.3% in a group with standard GDC and it was 41.7 +/- 31.7% in a group with GDC-HAp. These results indicated that coating by hydroxyapatite and bFGF might facilitate a wound healing in an experimental aneurysm model.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydroxyapatite coating of detachable coils for endovascular occlusion of experimental aneurysm.Interv Neuroradiol. 2001 Dec 22;7(Suppl 1):105-10. doi: 10.1177/15910199010070S115. Epub 2002 Jan 10. Interv Neuroradiol. 2001. PMID: 20663386 Free PMC article.
-
Development of the biologically active Guglielmi detachable coil for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Part II: an experimental study in a swine aneurysm model.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999 Nov-Dec;20(10):1992-9. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999. PMID: 10588133 Free PMC article.
-
Ion implantation and protein coating of detachable coils for endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms: concepts and preliminary results in swine models.Neurosurgery. 1997 Jun;40(6):1233-43; discussion 1243-4. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199706000-00024. Neurosurgery. 1997. PMID: 9179897
-
Selection of cerebral aneurysms for treatment using Guglielmi detachable coils: the preliminary University of Illinois at Chicago experience.Neurosurgery. 1998 Dec;43(6):1281-95; discussion 1296-7. doi: 10.1097/00006123-199812000-00011. Neurosurgery. 1998. PMID: 9848841 Review.
-
Follow-up angiography of intracranial aneurysms treated with endovascular placement of Guglielmi detachable coils.Neurosurgery. 2002 Feb;50(2):239-49; discussion 249-50. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200202000-00003. Neurosurgery. 2002. PMID: 11844258 Review.
References
-
- Bavinzski G, Talazoglu V, et al. Gross and microscopic histopathological findings in aneurysms of the human brain treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. J Neurosurg. 1999;91(2):284–293. - PubMed
-
- Dawson RC, Krisht AF, et al. Treatment of experimental aneurysms using collagen-coated microcoils. Neurosurgery. 1995;36(1):133–139. discussion 139-140. - PubMed
-
- Gruber A, Killer M, et al. Clinical and angiographic results of endosaccular coiling treatment of giant and very large intracranial aneurysms: a 7-year, single-center experience. Neurosurgery. 1999;45(4):793–803. discussion 803-794. - PubMed
-
- Kallmes DF, Helm GA, et al. Histologic evaluation of platinum coil embolization in an aneurysm model in rabbits. Radiology. 1999;213(1):217–222. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

