Double internal carotid origin of the ophthalmic artery with ruptured aneurysm of the posterior communicating artery. A case report
- PMID: 20591319
- PMCID: PMC3547381
- DOI: 10.1177/159101990300900409
Double internal carotid origin of the ophthalmic artery with ruptured aneurysm of the posterior communicating artery. A case report
Abstract
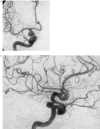
We report a case of double origin of the ophthalmic artery from the carotid siphon. The persistence of the primitive dorsal ophthalmic artery, together with a ventral ophthalmic artery, constitutes the double origin of the ophthalmic artery. Remnant of intraorbital anastomoses formed by these two arteries is demonstrated. This represents a rare configuration of double origin of the arterial blood supply, which is discovered "incidentally" in a patient harboring a ruptured aneurysm of the posterior communicating artery. The embryology of the ophthalmic artery and a possible association between vascular anomaly and arterial aneurysm can be envisaged.
Figures

References
-
- Padget DH. The development of the cranial arteries in the human embryo. Contrib Embryolo. 1948;32:207–262.
-
- Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A, terBrugge K. Surgical Neuroangiography. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer; 2002. pp. 414–455.
-
- Willinsky R, Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A. Intracavernous branches of the internal carotid artery (ICA). Comprehensive review of their variations. Surg Radiol Anat. 1987;9:201–215. - PubMed
-
- Hassler W, Zentner J, Voigt K. Abnormal origin of the ophthalmic artery from the anterior cerebral artery: neuroradiological and intraoperative findings. Neuroradiology. 1989;31:85–87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

