MicroRNA-181a modulates gene expression of zinc finger family members by directly targeting their coding regions
- PMID: 20591824
- PMCID: PMC2978345
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq564
MicroRNA-181a modulates gene expression of zinc finger family members by directly targeting their coding regions
Abstract
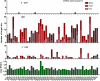
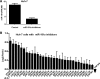
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small endogenous, non-coding RNAs that specifically bind to the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of target genes in animals. However, some recent studies have demonstrated that miRNAs also target the coding regions of mammalian genes. Here, we show that miRNA-181a downregulates the expression of a large number of zinc finger genes (ZNFs). Bioinformatics analysis revealed that these ZNFs contain many miR-181a seed-matched sites within their coding sequences (CDS). In particular, miR-181a 8-mer-matched sequences were mostly localized to the regions coding for the ZNF C2H2 domain. A series of reporter assays confirmed that miR-181a inhibits the expression of ZNFs by directly targeting their CDS. These inhibitory effects might be due to the multiple target sites located within the ZNF genes. In conclusion, our findings indicate that some miRNA species may regulate gene family by targeting their coding regions, thus providing an important and novel perspective for decoding the complex mechanism of miRNA/mRNA interplay.
Figures

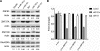

Similar articles
-
microRNA-181a is involved in insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated regulation of the transcription factor CREB1.J Neurochem. 2013 Sep;126(6):771-80. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12370. Epub 2013 Aug 6. J Neurochem. 2013. PMID: 23865718
-
MicroRNAs 29b and 181a down-regulate the expression of the norepinephrine transporter and glucocorticoid receptors in PC12 cells.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139(2):197-207. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13761. Epub 2016 Sep 22. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27501468 Free PMC article.
-
Atropa belladonna Expresses a microRNA (aba-miRNA-9497) Highly Homologous to Homo sapiens miRNA-378 (hsa-miRNA-378); both miRNAs target the 3'-Untranslated Region (3'-UTR) of the mRNA Encoding the Neurologically Relevant, Zinc-Finger Transcription Factor ZNF-691.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Jan;40(1):179-188. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00729-w. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31456135 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
The panorama of miRNA-mediated mechanisms in mammalian cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Jun;71(12):2253-70. doi: 10.1007/s00018-013-1551-6. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24468964 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-155 downregulates ErbB2 and suppresses ErbB2-induced malignant transformation of breast epithelial cells.Oncogene. 2016 Nov 17;35(46):6015-6025. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.132. Epub 2016 Apr 11. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 27065318
-
Overview of non-coding RNAs in breast cancers.Transl Oncol. 2022 Nov;25:101512. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2022.101512. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35961269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microRNA.Cell Res. 2012 Jan;22(1):107-26. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.158. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Cell Res. 2012. PMID: 21931358 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-200c modulates the expression of MUC4 and MUC16 by directly targeting their coding sequences in human pancreatic cancer.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 25;8(10):e73356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073356. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24204560 Free PMC article.
-
A high-resolution map of functional miR-181 response elements in the thymus reveals the role of coding sequence targeting and an alternative seed match.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 12;52(14):8515-8533. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae416. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38783381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120:15–20. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–531. - PubMed
-
- Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP. Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol. Cell. 2004;14:787–799. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

