MDM2 mediates ubiquitination and degradation of activating transcription factor 3
- PMID: 20592017
- PMCID: PMC2930690
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.132597
MDM2 mediates ubiquitination and degradation of activating transcription factor 3
Abstract
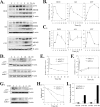
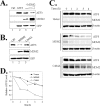
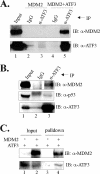
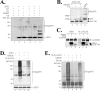
Activating transcription factor 3 (ATF3) is a common stress sensor, and its rapid induction by cellular stresses (e.g. DNA damage) is crucial for cells to mount appropriate responses (e.g. activating the tumor suppressor p53) and maintain homeostasis. Although emerging evidence suggests that dysregulation of ATF3 contributes to occurrences of human diseases including cancer, the mechanism(s) by which ATF3 expression is regulated is largely unknown. Here, we demonstrate that mouse double minute 2 (MDM2) is a bona fide E3 ubiquitin ligase for ATF3 and regulates ATF3 expression by promoting its degradation. MDM2 via its C-terminal RING finger can bind to the Basic region of ATF3 and mediate the addition of ubiquitin moieties to the ATF3 leucine zipper domain. As a consequence, ATF3, but not a mutant deficient in MDM2 binding (Delta80-100), is degraded by MDM2-mediated proteolysis. Consistent with these results, ablation of MDM2 in cells not only increases basal ATF3 levels, but results in stabilization of ATF3 in late stages of DNA damage responses. Because ATF3 was recently identified as a p53 activator, these results suggest that MDM2 could inactivate p53 through an additional feedback mechanism involving ATF3. Therefore, we provide the first evidence demonstrating that ATF3 is regulated by a posttranslational mechanism.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Competitive ubiquitination activates the tumor suppressor p53.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Jun;27(6):1807-1818. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0463-x. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 31796886 Free PMC article.
-
Activating transcription factor 3 activates p53 by preventing E6-associated protein from binding to E6.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 23;285(17):13201-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.058669. Epub 2010 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20167600 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Mdm2-p53 pathway by the ubiquitin E3 ligase MARCH7.EMBO Rep. 2018 Feb;19(2):305-319. doi: 10.15252/embr.201744465. Epub 2018 Jan 2. EMBO Rep. 2018. PMID: 29295817 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Mdm2-p53 loop: ubiquitin is the key.Cell Cycle. 2008 Feb 1;7(3):287-92. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.3.5358. Epub 2007 Nov 25. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18235222 Review.
-
p53 regulation: teamwork between RING domains of Mdm2 and MdmX.Cell Cycle. 2011 Dec 15;10(24):4225-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.10.24.18662. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Cell Cycle. 2011. PMID: 22134240 Review.
Cited by
-
The stress response mediator ATF3 represses androgen signaling by binding the androgen receptor.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;32(16):3190-202. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00159-12. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22665497 Free PMC article.
-
Deleting key autophagy elongation proteins induces acquirement of tumor-associated phenotypes via ISG15.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Aug;27(8):2517-2530. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0519-y. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 32127658 Free PMC article.
-
The Many Faces of MDM2 Binding Partners.Genes Cancer. 2012 Mar;3(3-4):226-39. doi: 10.1177/1947601912455322. Genes Cancer. 2012. PMID: 23150756 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Receptor PXR Confers Irradiation Resistance by Promoting DNA Damage Response Through Stabilization of ATF3.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 16;12:837980. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.837980. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35372071 Free PMC article.
-
A Legionella toxin exhibits tRNA mimicry and glycosyl transferase activity to target the translation machinery and trigger a ribotoxic stress response.Nat Cell Biol. 2023 Nov;25(11):1600-1615. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01248-z. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Nat Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37857833 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

