Temporal regulation of the muscle gene cascade by Macho1 and Tbx6 transcription factors in Ciona intestinalis
- PMID: 20592183
- PMCID: PMC2894658
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.066910
Temporal regulation of the muscle gene cascade by Macho1 and Tbx6 transcription factors in Ciona intestinalis
Abstract
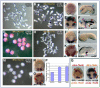
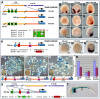
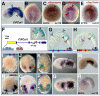
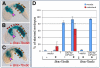
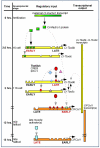
For over a century, muscle formation in the ascidian embryo has been representative of 'mosaic' development. The molecular basis of muscle-fate predetermination has been partly elucidated with the discovery of Macho1, a maternal zinc-finger transcription factor necessary and sufficient for primary muscle development, and of its transcriptional intermediaries Tbx6b and Tbx6c. However, the molecular mechanisms by which the maternal information is decoded by cis-regulatory modules (CRMs) associated with muscle transcription factor and structural genes, and the ways by which a seamless transition from maternal to zygotic transcription is ensured, are still mostly unclear. By combining misexpression assays with CRM analyses, we have identified the mechanisms through which Ciona Macho1 (Ci-Macho1) initiates expression of Ci-Tbx6b and Ci-Tbx6c, and we have unveiled the cross-regulatory interactions between the latter transcription factors. Knowledge acquired from the analysis of the Ci-Tbx6b CRM facilitated both the identification of a related CRM in the Ci-Tbx6c locus and the characterization of two CRMs associated with the structural muscle gene fibrillar collagen 1 (CiFCol1). We use these representative examples to reconstruct how compact CRMs orchestrate the muscle developmental program from pre-localized ooplasmic determinants to differentiated larval muscle in ascidian embryos.
Figures
References
-
- Aruga J., Kamiya A., Takahashi H., Fujimi T. J., Shimizu Y., Ohkawa K., Yazawa S., Umesono Y., Noguchi H., Shimizu T., et al. (2006). A wide-range phylogenetic analysis of Zic proteins: implications for correlations between protein structure conservation and body plan complexity. Genomics 87, 783-792 - PubMed
-
- Bertrand V., Hudson C., Caillol D., Popovici C., Lemaire P. (2004). Neural tissue in ascidian embryos is induced by FGF9/16/20, acting via a combination of maternal GATA and Ets transcription factors. Cell 115, 615-627 - PubMed
-
- Brown C. D., Johnson D. S., Sidow A. (2007). Functional architecture and evolution of transcriptional elements that drive gene coexpression. Science 317, 1557-1560 - PubMed
-
- Chapman D. L., Papaioannou V. E. (1998). Three neural tubes in mouse embryos with mutations in the T-box gene Tbx6. Nature 391, 695-697 - PubMed
-
- Christiaen L., Stolfi A., Davidson B., Levine M. (2009). Spatio-temporal intersection of Lhx3 and Tbx6 defines the cardiac field through synergistic activation of Mesp. Dev. Biol. 328, 552-560 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

