Endogenous signaling through alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors promotes maturation and integration of adult-born neurons in the hippocampus
- PMID: 20592195
- PMCID: PMC2905643
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0931-10.2010
Endogenous signaling through alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors promotes maturation and integration of adult-born neurons in the hippocampus
Abstract
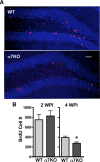
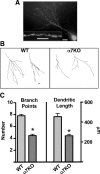
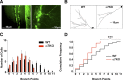
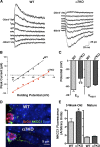
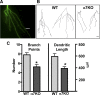
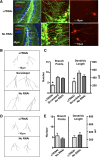
Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus occurs throughout adult mammalian life and is essential for proper hippocampal function. Early in their development, adult-born neurons express homomeric alpha7-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (alpha7-nAChRs) and receive direct cholinergic innervation. We show here that functional alpha7-nAChRs are necessary for normal survival, maturation, and integration of adult-born neurons in the dentate gyrus. Stereotaxic retroviral injection into the dentate gyrus of wild-type and alpha7-knock-out (alpha7KO) male and female mice was used to label and birthdate adult-born neurons for morphological and electrophysiological measures; BrdU (5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine) injections were used to quantify cell survival. In alpha7KO mice, we find that adult-born neurons develop with truncated, less complex dendritic arbors and display GABAergic postsynaptic currents with immature kinetics. The neurons also have a prolonged period of GABAergic depolarization characteristic of an immature state. In this condition, they receive fewer spontaneous synaptic currents and are more prone to die during the critical period when adult-born neurons are normally integrated into behaviorally relevant networks. Even those adult-born neurons that survive the critical period retain long-term dendritic abnormalities in alpha7KO mice. Interestingly, local infection with retroviral constructs to knockdown alpha7-mRNA mimics the alpha7KO phenotype, demonstrating that the relevant alpha7-nAChR signaling is cell autonomous. The results indicate a profound role for alpha7-nAChRs in adult neurogenesis and predict that alpha7-nAChR loss will cause progressive impairment in hippocampal circuitry and function over time as fewer neurons are added to the dentate gyrus and those that are added integrate less well.
Figures
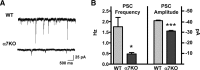

Similar articles
-
Functional alpha7 nicotinic receptors are expressed on immature granule cells of the postnatal dentate gyrus.Brain Res. 2015 Mar 19;1601:15-30. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.041. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25553616 Free PMC article.
-
The α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors regulate hippocampal adult-neurogenesis in a sexually dimorphic fashion.Brain Struct Funct. 2019 Mar;224(2):829-846. doi: 10.1007/s00429-018-1799-6. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Brain Struct Funct. 2019. PMID: 30515567 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in GABAergic neurons causes sex-dependent decreases in radial glia-like cell quantity and impairments in cognitive and social behavior.Brain Struct Funct. 2021 Mar;226(2):365-379. doi: 10.1007/s00429-020-02179-3. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Brain Struct Funct. 2021. PMID: 33398432 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic control of adult-born neuron fate.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Oct 15;82(8):820-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.06.021. Epub 2011 Jun 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21723854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the functional state of adult-born neurons in the adult dentate gyrus of the hippocampus: from birth to functional integration.Rev Neurosci. 2015;26(3):269-79. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2014-0071. Rev Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25781539 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-lasting changes in neural networks to compensate for altered nicotinic input.Biochem Pharmacol. 2015 Oct 15;97(4):418-424. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.07.020. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26206188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic deletion of α7 nAChRs reduces hippocampal granule and pyramidal cell number in both sexes but impairs pattern separation in males only.Front Neurosci. 2023 Sep 7;17:1244118. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1244118. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37746145 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic ACh receptors in the hippocampal circuit; functional expression and role in synaptic plasticity.J Physiol. 2014 Oct 1;592(19):4147-53. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.273896. Epub 2014 May 23. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24860170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stage-dependent alterations of progenitor cell proliferation and neurogenesis in an animal model of Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome.Brain Res. 2011 May 19;1391:132-46. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.03.048. Epub 2011 Apr 8. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21440532 Free PMC article.
-
Functional alpha7 nicotinic receptors are expressed on immature granule cells of the postnatal dentate gyrus.Brain Res. 2015 Mar 19;1601:15-30. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.041. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25553616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aimone JB, Wiles J, Gage FH. Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:723–727. - PubMed
-
- Aizawa H, Hu SC, Bobb K, Balakrishnan K, Ince G, Gurevich I, Cowan M, Ghosh A. Dendritic development regulated by CREST, a calcium-regulated transcriptional activator. Science. 2004;303:197–202. - PubMed
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque EX. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors α7 and α4β2 subtypes differentially control GABAergic input to CA1 neurons in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 2001;86:3043–3055. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
