Cooperation and heterogeneity of the autistic mind
- PMID: 20592203
- PMCID: PMC2907513
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0400-10.2010
Cooperation and heterogeneity of the autistic mind
Abstract
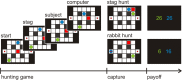
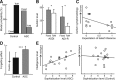
Individuals with autism spectrum conditions (ASCs) have a core difficulty in recursively inferring the intentions of others. The precise cognitive dysfunctions that determine the heterogeneity at the heart of this spectrum, however, remains unclear. Furthermore, it remains possible that impairment in social interaction is not a fundamental deficit but a reflection of deficits in distinct cognitive processes. To better understand heterogeneity within ASCs, we employed a game-theoretic approach to characterize unobservable computational processes implicit in social interactions. Using a social hunting game with autistic adults, we found that a selective difficulty representing the level of strategic sophistication of others, namely inferring others' mindreading strategy, specifically predicts symptom severity. In contrast, a reduced ability in iterative planning was predicted by overall intellectual level. Our findings provide the first quantitative approach that can reveal the underlying computational dysfunctions that generate the autistic "spectrum."
Figures

References
-
- Amaral DG, Schumann CM, Nordahl CW. Neuroanatomy of autism. Trends Neurosci. 2008;31:137–145. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Ed 4. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Baron-Cohen S, Belmonte MK. Autism: a window onto the development of the social and the analytic brain. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2005;28:109–126. - PubMed
-
- Beauchamp MH, Anderson V. SOCIAL: an integrative framework for the development of social skills. Psychol Bull. 2010;136:39–64. - PubMed
-
- Behrens TE, Hunt LT, Rushworth MF. The computation of social behavior. Science. 2009;324:1160–1164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
