Protein Phosphatase 2a and glycogen synthase kinase 3 signaling modulate prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response by altering cortical M-Type potassium channel activity
- PMID: 20592205
- PMCID: PMC3842471
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1292-10.2010
Protein Phosphatase 2a and glycogen synthase kinase 3 signaling modulate prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response by altering cortical M-Type potassium channel activity
Abstract
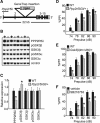
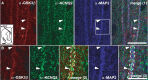
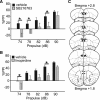
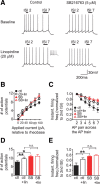
There is considerable interest in the regulation of sensorimotor gating, since deficits in this process could play a critical role in the symptoms of schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. Sensorimotor gating is often studied in humans and rodents using the prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle response (PPI) model, in which an acoustic prepulse suppresses behavioral output to a startle-inducing stimulus. However, the molecular and neural mechanisms underlying PPI are poorly understood. Here, we show that a regulatory pathway involving protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3beta), and their downstream target, the M-type potassium channel, regulates PPI. Mice (Mus musculus) carrying a hypomorphic allele of Ppp2r5delta, encoding a regulatory subunit of PP2A, show attenuated PPI. This PPP2R5delta reduction increases the phosphorylation of GSK3beta at serine 9, which inactivates GSK3beta, indicating that PPP2R5delta positively regulates GSK3beta activity in the brain. Consistently, genetic and pharmacological manipulations that reduce GSK3beta function attenuate PPI. The M-type potassium channel subunit, KCNQ2, is a putative GSK3beta substrate. Genetic reduction of Kcnq2 also reduces PPI, as does systemic inhibition of M-channels with linopirdine. Importantly, both the GSK3 inhibitor 3-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl)1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione (SB216763) and linopirdine reduce PPI when directly infused into the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Whole-cell electrophysiological recordings of mPFC neurons show that SB216763 and linopirdine have similar effects on firing, and GSK3 inhibition occludes the effects of M-channel inhibition. These data support a previously uncharacterized mechanism by which PP2A/GSK3beta signaling regulates M-type potassium channel activity in the mPFC to modulate sensorimotor gating.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PP2A-Bgamma subunit and KCNQ2 K+ channels in bipolar disorder.Pharmacogenomics J. 2007 Apr;7(2):123-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500400. Epub 2006 May 30. Pharmacogenomics J. 2007. PMID: 16733521
-
Neuronal coding of auditory sensorimotor gating in medial prefrontal cortex.Behav Brain Res. 2017 May 30;326:200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.03.004. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Behav Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28284946
-
Prefrontal inhibition of neuronal Kv 7 channels enhances prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle reflex and resistance to hypofrontality.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;177(20):4720-4733. doi: 10.1111/bph.15236. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32839968 Free PMC article.
-
Human studies of prepulse inhibition of startle: normal subjects, patient groups, and pharmacological studies.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001 Jul;156(2-3):234-58. doi: 10.1007/s002130100810. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2001. PMID: 11549226 Review.
-
Using an animal model of deficient sensorimotor gating to study the pathophysiology and new treatments of schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 1998;24(2):285-301. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.schbul.a033326. Schizophr Bull. 1998. PMID: 9613626 Review.
Cited by
-
GSK3 and β-catenin determines functional expression of sodium channels at the axon initial segment.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Jan;70(1):105-20. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1059-5. Epub 2012 Jul 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22763697 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of c-Myc Protein Abundance by a Protein Phosphatase 2A-Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β-Negative Feedback Pathway.Genes Cancer. 2012 Jan;3(1):23-36. doi: 10.1177/1947601912448067. Genes Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22893788 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Schizophrenia Susceptibility Gene Ulk4 Leads to Abnormal Cognitive Behaviors via Akt-GSK-3 Signaling Pathway in Mice.Schizophr Bull. 2022 Jun 21;48(4):804-813. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbac040. Schizophr Bull. 2022. PMID: 35522199 Free PMC article.
-
The role of serine/threonine phosphatases in human development: Evidence from congenital disorders.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 13;10:1030119. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1030119. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36313552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ppp2r2a Knockout Mice Reveal That Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulatory Subunit, PP2A-B55α, Is an Essential Regulator of Neuronal and Epidermal Embryonic Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 5;8:358. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00358. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32582689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aghdam SY, Barger SW. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection: lessons from lithium. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007;4:21–31. - PubMed
-
- Alimohamad H, Rajakumar N, Seah YH, Rushlow W. Antipsychotics alter the protein expression levels of beta-catenin and GSK-3 in the rat medial prefrontal cortex and striatum. Biol Psychiatry. 2005a;57:533–542. - PubMed
-
- Alimohamad H, Sutton L, Mouyal J, Rajakumar N, Rushlow WJ. The effects of antipsychotics on beta-catenin, glycogen synthase kinase-3 and dishevelled in the ventral midbrain of rats. J Neurochem. 2005b;95:513–525. - PubMed
-
- Amar S, Jones BC, Nadri C, Kozlovsky N, Belmaker RH, Agam G. Genetic correlational analysis of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and prepulse inhibition in inbred mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2004;3:178–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
