Genomic architecture characterizes tumor progression paths and fate in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 20592421
- PMCID: PMC3972440
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000611
Genomic architecture characterizes tumor progression paths and fate in breast cancer patients
Abstract
Distinct molecular subtypes of breast carcinomas have been identified, but translation into clinical use has been limited. We have developed two platform-independent algorithms to explore genomic architectural distortion using array comparative genomic hybridization data to measure (i) whole-arm gains and losses [whole-arm aberration index (WAAI)] and (ii) complex rearrangements [complex arm aberration index (CAAI)]. By applying CAAI and WAAI to data from 595 breast cancer patients, we were able to separate the cases into eight subgroups with different distributions of genomic distortion. Within each subgroup data from expression analyses, sequencing and ploidy indicated that progression occurs along separate paths into more complex genotypes. Histological grade had prognostic impact only in the luminal-related groups, whereas the complexity identified by CAAI had an overall independent prognostic power. This study emphasizes the relation among structural genomic alterations, molecular subtype, and clinical behavior and shows that objective score of genomic complexity (CAAI) is an independent prognostic marker in breast cancer.
Figures
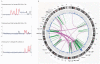
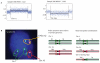
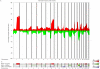
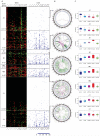
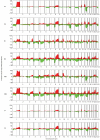
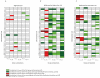

Comment in
-
Genomics: A broad brush.Nat Rev Cancer. 2010 Sep;10(9):600. doi: 10.1038/nrc2920. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20803811 No abstract available.
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365:1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de RM, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–752. - PubMed
-
- Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de RM, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Eystein LP, Borresen-Dale AL. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2001;98:10869–10874. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sorlie T, Tibshirani R, Parker J, Hastie T, Marron JS, Nobel A, Deng S, Johnsen H, Pesich R, Geisler S, Demeter J, Perou CM, Lonning PE, Brown PO, Borresen-Dale AL, Botstein D. Repeated observation of breast tumor subtypes in independent gene expression data sets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2003;100:8418–8423. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, Karaca G, Troester MA, Tse CK, Edmiston S, Deming SL, Geradts J, Cheang MC, Nielsen TO, Moorman PG, Earp HS, Millikan RC. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 2006;295:2492–2502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

