IL-12-STAT4-IFN-gamma axis is a key downstream pathway in the development of IL-13-mediated asthma phenotypes in a Th2 type asthma model
- PMID: 20592486
- PMCID: PMC2928926
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2010.42.8.054
IL-12-STAT4-IFN-gamma axis is a key downstream pathway in the development of IL-13-mediated asthma phenotypes in a Th2 type asthma model
Abstract
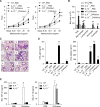
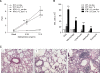
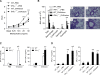
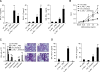
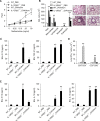
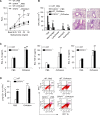
IL-4 and IL-13 are closely related cytokines that are produced by Th2 cells. However, IL-4 and IL-13 have different effects on the development of asthma phenotypes. Here, we evaluated downstream molecular mechanisms involved in the development of Th2 type asthma phenotypes. A murine model of Th2 asthma was used that involved intraperitoneal sensitization with an allergen (ovalbumin) plus alum and then challenge with ovalbumin alone. Asthma phenotypes, including airway-hyperresponsiveness (AHR), lung inflammation, and immunologic parameters were evaluated after allergen challenge in mice deficient in candidate genes. The present study showed that methacholine AHR and lung inflammation developed in allergen-challenged IL-4-deficient mice but not in allergen-challenged IL-13-deficient mice. In addition, the production of OVA-specific IgG2a and IFN-gamma-inducible protein (IP)-10 was also impaired in the absence of IL-13, but not of IL-4. Lung-targeted IFN-gamma over-expression in the airways enhanced methacholine AHR and non-eosinophilic inflammation; in addition, these asthma phenotypes were impaired in allergen-challenged IFN-gamma-deficient mice. Moreover, AHR, non-eosinophilic inflammation, and IFN-gamma expression were impaired in allergen-challenged IL-12Rbeta2- and STAT4-deficient mice; however, AHR and non-eosinophilic inflammation were not impaired in allergen-challenged IL-4Ralpha-deficient mice, and these phenomena were accompanied by the enhanced expression of IL-12 and IFN-gamma. The present data suggest that IL-13-mediated asthma phenotypes, such as AHR and non-eosinophilic inflammation, in the Th2 type asthma are dependent on the IL-12-STAT4-IFN-gamma axis, and that these asthma phenotypes are independent of IL-4Ralpha-mediated signaling.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adenovirus-mediated interferon gamma gene therapy for allergic asthma: involvement of interleukin 12 and STAT4 signaling.Hum Gene Ther. 2002 Sep 20;13(14):1697-709. doi: 10.1089/104303402760293547. Hum Gene Ther. 2002. PMID: 12396623
-
Attenuated expression of tenascin-C in ovalbumin-challenged STAT4-/- mice.Respir Res. 2011 Jan 4;12(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-12-2. Respir Res. 2011. PMID: 21205293 Free PMC article.
-
4-1 BB stimulation inhibits allergen-specific immunoglobulin E production and airway hyper-reactivity but partially suppresses bronchial eosinophilic inflammation in a mouse asthma model.Clin Exp Allergy. 2006 Mar;36(3):377-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02445.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2006. PMID: 16499650
-
Role of IgE in the development of allergic airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness--a murine model.Allergy. 1999 Apr;54(4):297-305. doi: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.1999.00085.x. Allergy. 1999. PMID: 10371087 Review.
-
The genetics of allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in mice.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997 Oct;156(4 Pt 2):S89-96. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.156.4.12-tac-3. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997. PMID: 9351586 Review.
Cited by
-
T(H)17 cells mediate pulmonary collateral priming.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 Jul;128(1):168-177.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.01.067. Epub 2011 Apr 2. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21459426 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 13 and the evolution of asthma therapy.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2012 Jun 30;1(1):20-27. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23607082 Free PMC article.
-
A hypothesis-effect of T cell epitope fusion peptide specific immunotherapy on signal transduction.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Oct 15;8(10):19632-4. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26770626 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-derived growth factor mediates interleukin-13-induced collagen I production in mouse airway fibroblasts.J Biosci. 2014 Sep;39(4):693-700. doi: 10.1007/s12038-014-9454-8. J Biosci. 2014. PMID: 25116623
-
Pulmonary IFN-γ Causes Lymphocytic Inflammation and Cough Hypersensitivity by Increasing the Number of IFN-γ-Secreting T Lymphocytes.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022 Nov;14(6):653-673. doi: 10.4168/aair.2022.14.6.653. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36426396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aman MJ, Tayebi N, Obiri NI, Puri RK, Modi WS, Leonard WJ. cDNA cloning and characterization of the human interleukin 13 receptor alpha chain. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:29265–29270. - PubMed
-
- Caput D, Laurent P, Kaghad M, Lelias JM, Lefort S, Vita N, Ferrara P. Cloning and characterization of a specific interleukin (IL)-13 binding protein structurally related to the IL-5 receptor alpha chain. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:16921–16926. - PubMed
-
- Cohn L, Tepper JS, Bottomly K. IL-4-independent induction of airway hyperresponsiveness by Th2, but not Th1, cells. J Immunol. 1998;161:3813–3816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
