Siroheme: an essential component for life on earth
- PMID: 20592802
- PMCID: PMC2835951
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.5.1.10173
Siroheme: an essential component for life on earth
Abstract
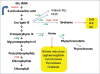
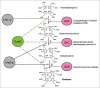
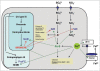
Life on earth is dependent on sulphur (S) and nitrogen (N). In plants, the second step in the reduction of sulphate and nitrate are mediated by the enzymes sulphite and nitrite reductases, which contain the iron (Fe)-containing siroheme as a cofactor. It is synthesized from the tetrapyrrole primogenitor uroporphyrinogen III in the plastids via three enzymatic reactions, methylation, oxidation and ferrochelatation. Without siroheme biosynthesis, there would be no life on earth. Limitations in siroheme should have an enormous effect on the S- and N-metabolism, plant growth, development, fitness and reproduction, biotic and abiotic stresses including growth under S, N and Fe limitations, and the response to pathogens and beneficial interaction partners. Furthermore, the vast majority of redox-reactions in plants depend on S-components, and S-containing compounds are also involved in the detoxification of heavy metals and other chemical toxins. Disturbance of siroheme biosynthesis may cause the accumulation of light-sensitive intermediates and reactive oxygen species, which are harmful, or they can function as signaling molecules and participate in interorganellar signaling processes. This review highlights the role of siroheme in these scenarios.
Keywords: iron; nitrogen; plant/microbe interaction; redox; siroheme; sulphur.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of the terminal enzyme of siroheme biosynthesis from Arabidopsis thaliana: a plastid-located sirohydrochlorin ferrochelatase containing a 2FE-2S center.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 11;280(6):4713-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411360200. Epub 2004 Nov 15. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15545265
-
Pathways of Iron and Sulfur Acquisition, Cofactor Assembly, Destination, and Storage in Diverse Archaeal Methanogens and Alkanotrophs.J Bacteriol. 2021 Aug 9;203(17):e0011721. doi: 10.1128/JB.00117-21. Epub 2021 Aug 9. J Bacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34124941 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative pathways for siroheme synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes.J Bacteriol. 2001 Jan;183(1):328-35. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.1.328-335.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11114933 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in higher plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2007;58:321-46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105448. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2007. PMID: 17227226 Review.
-
The biology of reactive sulfur species (RSS).Plant Physiol Biochem. 2012 Oct;59:98-107. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.03.016. Epub 2012 Apr 7. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22541352 Review.
Cited by
-
Chlorophyll biosynthesis gene evolution indicates photosystem gene duplication, not photosystem merger, at the origin of oxygenic photosynthesis.Genome Biol Evol. 2013;5(1):200-16. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evs127. Genome Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23258841 Free PMC article.
-
Young Leaf Chlorosis 2 encodes the stroma-localized heme oxygenase 2 which is required for normal tetrapyrrole biosynthesis in rice.Planta. 2014 Oct;240(4):701-12. doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2116-0. Epub 2014 Jul 19. Planta. 2014. PMID: 25037719
-
Critical parameters and procedures for anaerobic cultivation of yeasts in bioreactors and anaerobic chambers.FEMS Yeast Res. 2021 Jun 21;21(5):foab035. doi: 10.1093/femsyr/foab035. FEMS Yeast Res. 2021. PMID: 34100921 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrapyrroles as Endogenous TSPO Ligands in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes: Comparisons with Synthetic Ligands.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 4;17(6):880. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060880. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27271616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Siroheme Is Essential for Assimilation of Nitrate and Sulfate as Well as Detoxification of Nitric Oxide but Dispensable for Murine Virulence of Aspergillus fumigatus.Front Microbiol. 2018 Nov 12;9:2615. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02615. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30483221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leustek T, Martin MN, Bick JA, Davies JP. Pathways and regulation of sulfur metabolism revealed through molecular and genetic studies. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol. 2000;51:141–165. - PubMed
-
- Sato S, Soga T, Nishioka T, Tomita M. Simultaneous determination of the main metabolites in rice leaves using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry and capillary electrophoresis diode array detection. Plant J. 2004;40:151–163. - PubMed
-
- Kopriva S, Wiedemann G, Reski R. Sulphate assimilation in basal land plants–what does genomic sequencing tell us? Plant Biol. 2007;9:556–564. - PubMed
-
- Höfgen R, Kreft O, Willmitzer L, Hesse H. Manipulation of thiol contents in plants. Amino Acids. 2001;20:291–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
