Role of histone methylation and demethylation in adipogenesis and obesity
- PMID: 20592862
- PMCID: PMC2861740
- DOI: 10.4161/org.6.1.11121
Role of histone methylation and demethylation in adipogenesis and obesity
Abstract
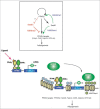
Adipocyte differentiation is a complex developmental process that involves the coordinated interplay of numerous transcription factors. PPARγ has emerged as a master regulator of adipogenesis and recent global target gene analysis demonstrated that PPARγ targets many genes encoding chromatin modification enzymes as well as genes of lipid metabolism and storage. Among such modification enzymes are histone lysine methyltransferases, which play important roles in transcriptional regulation. Histone methyltransferases are involved in PPARγ gene expression and subsequent adipogenesis. In addition, recent studies revealed that demethylation of histone H3 at lys9 is associated with resistance to obesity. We here review the role of histone methylation and demethylation in adipogenesis, metabolism and obesity.
Keywords: PR-Set7; Setd8; Setdb1; Wnt; adipogenesis; epigenetics; histone lysine methyltransferase (HKMT); metabolic syndrome; obesity; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR).
Figures


Similar articles
-
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma/retinoid X receptor alpha heterodimer targets the histone modification enzyme PR-Set7/Setd8 gene and regulates adipogenesis through a positive feedback loop.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Jul;29(13):3544-55. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01856-08. Epub 2009 May 4. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19414603 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H3K9 methyltransferase G9a represses PPARγ expression and adipogenesis.EMBO J. 2013 Jan 9;32(1):45-59. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.306. Epub 2012 Nov 23. EMBO J. 2013. PMID: 23178591 Free PMC article.
-
PPARγ and Wnt Signaling in Adipogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(3):216-25. doi: 10.2174/1574888x10666150519093429. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 25986621 Review.
-
Quercetin and its derivative Q2 modulate chromatin dynamics in adipogenesis and Q2 prevents obesity and metabolic disorders in rats.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Jul;69:151-162. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.03.019. Epub 2019 Apr 8. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31096072
-
Genetic and epigenetic regulation of PPARγ during adipogenesis.Yi Chuan. 2017 Nov 20;39(11):1066-1077. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-121. Yi Chuan. 2017. PMID: 29254924 Review.
Cited by
-
ANRIL: molecular mechanisms and implications in human health.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jan 10;14(1):1278-92. doi: 10.3390/ijms14011278. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23306151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factors and their potential role in cardiac epigenetics.J Cell Mol Med. 2016 Aug;20(8):1589-602. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12845. Epub 2016 Apr 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27061217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DHT causes liver steatosis via transcriptional regulation of SCAP in normal weight female mice.J Endocrinol. 2021 Jun 28;250(2):49-65. doi: 10.1530/JOE-21-0040. J Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34060475 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of SUV39H1 and CITED2 Exerts Additive Effect on Promoting Adipogenic Commitment of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2021 May 1;30(9):485-501. doi: 10.1089/scd.2020.0190. Epub 2021 Apr 13. Stem Cells Dev. 2021. PMID: 33691475 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics lights up the obesity field.Obes Facts. 2011;4(3):187-90. doi: 10.1159/000329847. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Obes Facts. 2011. PMID: 21701233 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wolffe AP. Transcriptional regulation in the context of chromatin structure. Essays Biochem. 2001;37:45–57. - PubMed
-
- Kornberg RD, Lorch Y. Twenty-five years of the nucleosome, fundamental particle of the eukaryote chromosome. Cell. 1999;98:285–294. - PubMed
-
- Jenuwein T, Allis CD. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293:1074–1080. - PubMed
-
- Fischle W, Wang Y, Allis CD. Histone and chromatin cross-talk. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:172–183. - PubMed
-
- Margueron R, Trojer P, Reinberg D. The key to development: interpreting the histone code? Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2005;15:163–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
