THE STABILITY OF PSYCHOPATHY FROM ADOLESCENCE INTO ADULTHOOD: The Search for Moderators
- PMID: 20593007
- PMCID: PMC2893343
- DOI: 10.1177/0093854807310153
THE STABILITY OF PSYCHOPATHY FROM ADOLESCENCE INTO ADULTHOOD: The Search for Moderators
Abstract
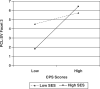
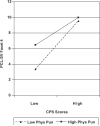
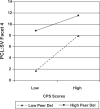
This study examines moderators of the relation between psychopathy assessed at age 13 using the mother-reported Childhood Psychopathy Scale and psychopathy assessed at age 24 using the interviewer-rated Psychopathy Checklist: Screening Version (PCL:SV). Data from more than 250 participants of the middle sample of the Pittsburgh Youth Study were used. Thirteen potential moderators were examined, including demographics (i.e., race, family structure, family socioeconomic status [SES], and neighborhood SES), parenting factors (physical punishment, inconsistent discipline, lax supervision, and positive parenting), peer delinquency, own delinquency, and other individual differences (i.e., verbal IQ, behavioral impulsivity, and cognitive impulsivity). Moderators were examined for the total psychopathy score at age 24 as well as for each of the four PCL:SV facets. After relaxing the criterion for statistical significance, 8 out of a possible 65 interactions were statistically significant. Implications of the present findings and future directions are discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Psychopathy in Adolescence Predicts Official Reports of Offending in Adulthood.Youth Violence Juv Justice. 2009 Jul 1;7(3):189-207. doi: 10.1177/1541204009333797. Epub 2009 May 11. Youth Violence Juv Justice. 2009. PMID: 22661910 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal evidence that psychopathy scores in early adolescence predict adult psychopathy.J Abnorm Psychol. 2007 Feb;116(1):155-65. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.116.1.155. J Abnorm Psychol. 2007. PMID: 17324026 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive impulsivity and the development of delinquency from late childhood to early adulthood: Moderating effects of parenting behavior and peer relationships.Dev Psychopathol. 2016 Feb;28(1):167-83. doi: 10.1017/S095457941500036X. Epub 2015 May 6. Dev Psychopathol. 2016. PMID: 25997462
-
Psychometric Properties in Forensic Application of the Screening Version of the Psychopathy Checklist.Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2018 May;62(7):1869-1887. doi: 10.1177/0306624X17719289. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2018. PMID: 28741393 Review.
-
[The psychopathy-concept and its psychometric evaluation in childhood, adolescence and adulthood].Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2005 Jul;73(7):392-400. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-830153. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 2005. PMID: 16012918 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Psychopathy in Adolescence Predicts Official Reports of Offending in Adulthood.Youth Violence Juv Justice. 2009 Jul 1;7(3):189-207. doi: 10.1177/1541204009333797. Epub 2009 May 11. Youth Violence Juv Justice. 2009. PMID: 22661910 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Emotion Understanding in the Development of Aggression and Callous-Unemotional Features across Early Childhood.J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2019 Apr;47(4):619-631. doi: 10.1007/s10802-018-0468-9. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2019. PMID: 30155686
-
Mediation of the relationship between callous-unemotional traits and proactive aggression by amygdala response to fear among children with conduct problems.JAMA Psychiatry. 2014 Jun;71(6):627-36. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.4540. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 24671141 Free PMC article.
-
The Relative Importance of Psychopathy Features as Predictors of Externalizing Behaviors in Youth: A Multimethod Examination.J Psychopathol Behav Assess. 2023 Mar;45(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s10862-022-10017-5. Epub 2023 Jan 30. J Psychopathol Behav Assess. 2023. PMID: 37691858 Free PMC article.
-
A Validation of the Inventory of Callous-Unemotional Traits in a Community Sample of Young Adult Males.J Psychopathol Behav Assess. 2013 Mar 1;35(1):10.1007/s10862-012-9315-4. doi: 10.1007/s10862-012-9315-4. J Psychopathol Behav Assess. 2013. PMID: 24357894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiken LS, West SG. Multiple regression: Testing and interpreting interactions. Sage; Newbury Park, CA: 1991.
-
- Alterman A, Cacciola J, Rutherford M. Reliability of the Revised Psychopathy Checklist in substance abuse patients. Psychological Assessment. 1993;5:442–448.
-
- Arseneault L, Tremblay RE, Boulerice B, Seguin JR, Saucier JF. Obstetrical complications and violent delinquency: Testing two developmental pathways. Child Development. 2002;73:496–508. - PubMed
-
- Blair RJR, Coles M. Expression recognition and behavioural problems in early adolescence. Cognitive Development. 2000;15:421–434.
-
- Brennan PA, Mednick SA, Raine A. Biosocial interactions and violence: A focus on perinatal factors. In: Raine A, Brennan PA, Farrington DP, Mednick SA, editors. Biosocial bases of violence. Plenum; New York: 1997. pp. 163–174.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
