2-Deoxy-D-glucose activates autophagy via endoplasmic reticulum stress rather than ATP depletion
- PMID: 20593179
- PMCID: PMC3093301
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-010-1391-0
2-Deoxy-D-glucose activates autophagy via endoplasmic reticulum stress rather than ATP depletion
Abstract
Purpose: The glucose analog and glycolytic inhibitor 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG), which is currently under clinical evaluation for targeting cancer cells, not only blocks glycolysis thereby reducing cellular ATP, but also interferes with N-linked glycosylation, which leads to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and an unfolded protein response (UPR). Both bioenergetic challenge and ER stress have been shown to activate autophagy, a bulk cellular degradation process that plays either a pro- or anti-death role. Here, we investigate which pathway 2-DG interferes with that activates autophagy and the role of this process in modulating 2-DG-induced toxicity.
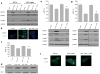
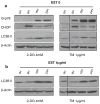
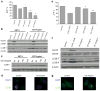
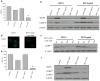
Methods: Pancreatic cancer cell line 1420, melanoma cell line MDA-MB-435 and breast cancer cell line SKBR3 were used to investigate the relationship between induction by 2-DG treatment of ER stress/UPR, ATP reduction and activation of autophagy. ER stress/UPR (Grp78 and CHOP) and autophagy (LC3B II) markers were assayed by immunoblotting, while ATP levels were measured using the CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay. Autophagy was also measured by immunofluorescence utilizing LC3B antibody. Cell death was detected with a Vi-Cell cell viability analyzer using trypan blue exclusion.
Results: In the three different cancer cell lines described earlier, we find that 2-DG upregulates autophagy, increases ER stress and lowers ATP levels. Addition of exogenous mannose reverses 2-DG-induced autophagy and ER stress but does not recover the lowered levels of ATP. Moreover, under anaerobic conditions where 2-DG severely depletes ATP, autophagy is diminished rather than activated, which correlates with lowered levels of the ER stress marker Grp78. Additionally, when autophagy is blocked by siRNA, cell sensitivity to 2-DG is increased corresponding with upregulation of ER stress-mediated apoptosis. Similar increased toxicity is observed with 3-methyladenine, a known autophagy inhibitor. In contrast, rapamycin which enhances autophagy reduces 2-DG-induced toxicity.
Conclusions: Overall, these results indicate that the major mechanism by which 2-DG stimulates autophagy is through ER stress/UPR and not by lowering ATP levels. Furthermore, autophagy plays a protective role against 2-DG-elicited cell death apparently by relieving ER stress. These data suggest that combining autophagy inhibitors with 2-DG may be useful clinically.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Wick AN, Drury DR, Nakada HI, Wolfe JB. Localization of the primary metabolic block produced by 2-deoxyglucose. J Biol Chem. 1957;224:963–969. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Gueron M. The inhibition of bovine heart hexokinase by 2-deoxy-D-glucose-6-phosphate: characterization by 31P NMR and metabolic implications. Biochimie. 1992;74:867–873. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Hu YP, Savaraj N, Priebe W, Lampidis TJ. Hypersensitization of tumor cells to glycolytic inhibitors. Biochemistry. 2001;40:5542–5547. - PubMed
-
- Liu H, Savaraj N, Priebe W, Lampidis TJ. Hypoxia increases tumor cell sensitivity to glycolytic inhibitors: a strategy for solid tumor therapy (model C) Biochem Pharmacol. 2002;64:1745–1751. - PubMed
-
- Maher JC, Krishan A, Lampidis TJ. Greater cell cycle inhibition and cytotoxicity induced by 2-deoxy-D-glucose in tumor cells treated under hypoxic vs aerobic conditions. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2004;53:116–122. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

