Nanoparticle-mediated brain-specific drug delivery, imaging, and diagnosis
- PMID: 20593303
- PMCID: PMC2933363
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-010-0141-7
Nanoparticle-mediated brain-specific drug delivery, imaging, and diagnosis
Abstract
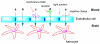
Central nervous system (CNS) diseases represent the largest and fastest-growing area of unmet medical need. Nanotechnology plays a unique instrumental role in the revolutionary development of brain-specific drug delivery, imaging, and diagnosis. With the aid of nanoparticles of high specificity and multifunctionality, such as dendrimers and quantum dots, therapeutics, imaging agents, and diagnostic molecules can be delivered to the brain across the blood-brain barrier (BBB), enabling considerable progress in the understanding, diagnosis, and treatment of CNS diseases. Nanoparticles used in the CNS for drug delivery, imaging, and diagnosis are reviewed, as well as their administration routes, toxicity, and routes to cross the BBB. Future directions and major challenges are outlined.
Figures

References
-
- Johnson N, Davis T, Bosanquet N. The epidemic of Alzheimer's disease. How can we manage the costs? Pharmacoeconomics. 2000;18:215–23. - PubMed
-
- Pardridge WM. Blood-brain barrier biology and methodology. J Neurovirol. 1999;5:556–69. - PubMed
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Smith QR, Rapoport SI. Cerebrovascular permeability coefficients to sodium, potassium, and chloride. J Neurochem. 1986;46:1732–42. - PubMed
-
- Pardridge WM, Buciak JL, Friden PM. Selective transport of an anti-transferrin receptor antibody through the blood-brain barrier in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991;259:66–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

